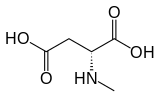
 |
“N-Methyl-D-asparaginsäure oder N-Methyl-D-aspartat (NMDA) ist ein Aminosäurederivat, das als spezifischer Agonist am NMDA-Rezeptor wirkt und die Wirkung von Glutamat nachahmt, dem Neurotransmitter, der normalerweise an diesem Rezeptor wirkt. Im Gegensatz zu Glutamat bindet und reguliert NMDA nur den NMDA-Rezeptor und hat keinen Einfluss auf andere Glutamatrezeptoren (z.B. für AMPA und Kainat). NMDA-Rezeptoren sind besonders wichtig, wenn sie während des Alkoholentzuges überaktiv werden, da dies Symptome wie Unruhe und manchmal epileptische Anfälle verursacht.
N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid or N-Methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) is an amino acid derivative that acts as a specific agonist at the NMDA receptor mimicking the action of glutamate, the neurotransmitter which normally acts at that receptor. Unlike glutamate, NMDA only binds to and regulates the NMDA receptor and has no effect on other glutamate receptors (such as those for AMPA and kainate). NMDA receptors are particularly important when they become overactive during withdrawal from alcohol as this causes symptoms such as agitation and, sometimes, epileptiform seizures.
Contents
Stand vom … ” → Wp
Hauptquellen der Texte und Materialien:
Internationale Wikipedias. Wurde evtl. ganz oder teilweise ins Deutsche übersetzt. Unter der Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 4.0 verfügbar; zusätzliche Bedingungen können gelten. Durch die Nutzung dieser Website erklären Sie sich mit den Nutzungsbedingungen und der Datenschutzrichtlinie einverstanden.
Weitere extensive und evtl. aktuellere Ausführungen finden Sie in den zitierten Wikipedia-Artikeln.