Letzte PostsPopulärKategorienGlossarSchlagwortePagesGeändertArchiveKommentareSocial MediaInfo-Krümel
Einige Kategorien:
Ernährung
Du bist, was du isst
Gehirn
Immunsystem
Du bist, was du isst
Medizin
Du bist, was du isst
Ökologie
Tooltip-Glossar
- Präbiotika
- Metastase
- Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methybutyrate
- Acesulfam-K
- Acrolein
- Actinobacteria
- Addressin
- Adipozyt
- Advantam
- Aggression
- Akupunktur
- Albert Einstein
- Aldehyd-Dehydrogenase 2
- Aldehyde
- Alkalische Phosphatase
- Allergie
- Allesfresser
- Alpha-Synuclein
- Alzheimer-Krankheit
- Aminosäuren
- Amygdala
- Amyloidose
- Anämie
- Anatomie
- Angiotensin-konvertierendes Enzym 2
- Antioxidans
- AP-1
- Apoptose
- Arachidonsäure
- Asaccharobacter celatus
- Aspartam
- Astrozyt
- Atherosklerose
- Autoimmunerkrankung
- Autophagozytose
- B-Lymphozyt
- Bacillus subtilis
- Bacteriocine
- Bacteroides fragilis
- Bacteroidetes
- Bakterien
- Bakteriophagen
- Beclin-1
- Benediktenkraut
- Bewegungswissenschaft
- Bifidobacterium
- Bindegewebe
- Biodiversität
- Biogene Amine
- Biolumineszenz
- Biomarker
- Bipolare Störung
- Bisphenol A
- Blinddarm
- Blut-Hirn-Schranke
- Blutgruppe
- Body-Mass-Index
- Bray-Curtis-Unähnlichkeit
- Butyrat
- C-reaktives Protein
- Caco-2
- CAR-T-Zell-Therapie
- Carbonylgruppe
- CC BY-NC-ND 4.0
- CD1
- CD4-Rezeptor
- CD8-Rezeptor
- CD44-Antigen
- Chloroplast
- Chromosom
- Chromosomal fragile site
- Chronisch-entzündliche Darmerkrankungen
- Clostridien
- Clostridium scindens
- Cobalamine
- Colitis ulcerosa
- Cookie
- Corynebacterium
- COVID-19
- COVID-19-Pandemie
- Creative Commons
- Creative Commons CC BY-SA 3.0
- CRISPR/Cas-Methode
- Cutibacterium acnes
- CXCL16
- Darm
- Darmflora
- Darmschleimhaut
- Default Mode Network
- Demenz
- Demyelinisierende Erkrankung
- Depression
- Desoxyribonukleinsäure
- Diabetes mellitus
- DNA-Sequenzierung
- Drosophila melanogaster
- Dünndarm
- Dünndarm
- Dünnschichtchromatographie
- Effluxpumpe
- Ekzem
- Elektroanalytik
- Elektronenmikroskop
- Elektronentransportkette
- Endoplasmatisches Retikulum
- Enterisches Nervensystem
- Enterobacteriaceae
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Enterozyt
- Entscheidung
- Entzündung
- Entzündungsaltern
- Enzym
- Epigenetik
- Equol
- Escherichia coli
- Ethanol
- Farbratte
- Fast Food
- Fasten
- Fermentation
- Fette
- Fettgewebe
- Fettleibigkeit
- Fettsäuren
- Fibrinogen
- Fibroblast
- Fibrose
- Firmicutes
- Flagelline
- Fleisch
- Fließinjektionsanalyse
- Follikuläre B-Helfer-T-Zellen
- Folsäure
- Fornix (Gehirn)
- Furcht
- Fusobacteriales
- G-Protein-gekoppelte Rezeptoren
- Galle
- Gallensäuren
- Gamma-Aminobuttersäure
- Gaschromatographie
- Gedächtnis
- Gehirn
- Gemeinfreiheit
- Gen
- Genexpression
- Genlocus
- Genom
- Glucocorticoide
- Glucose
- Glukosespiegel
- Glutamatrezeptor
- Glutathion
- Glutathionperoxidase
- Glykogen
- Glykoprotein CD14
- Gnotobiose
- Granulozyt
- Gyrus cinguli
- Cannabis als Rauschmittel
- Hefen
- Helicobacter pylori
- Heparansulfat
- Herz-Kreislauf-Erkrankung
- Hippocampus
- Histamin
- Histamin-Intoleranz
- Histologie
- Hochleistungsflüssigkeitschromatographie
- Homer Simpson
- Homocystein
- Homöostase
- Horizontaler Gentransfer
- Hormon
- HPA-Achse
- Hydroxycarbonsäure-Rezeptor 1-3
- Hydroxycarbonsäuren
- Hypothalamus
- Immunglobulin A
- Immunsystem
- in vitro
- in vivo
- Inflammasom
- Inokulation
- Inokulum
- Inselrinde
- Insulin
- Insulinresistenz
- Interferon-γ
- Interleukin-1β
- Interleukin-10
- Interleukin 22
- Interleukine
- Intraepitheliale Lymphozyten
- Ionenaustauschchromatographie
- Kaiserschnitt
- Kalorienrestriktion
- Kapillarelektrophorese
- Kavernom
- Kefir
- Ketogene Diät
- Ketokörper
- Ketone
- Ki-67 (Protein)
- Kimchi
- Klassenwechsel
- Klastogen
- Knochenmark
- Kocuria
- Kognition
- Kohlenhydrate
- Kombucha
- Kommensalismus
- Konjugierte Linolsäuren
- Kontamination
- Krebs
- Lactobacillus
- Langzeit-Potenzierung
- Leaky-Gut-Syndrom
- Leber
- Lernen
- Leucin
- Leukozyt
- Lewy-Körperchen
- Linolsäure
- Lipidperoxidation
- Liponsäure
- Lipopolysaccharid-bindendes-Protein
- Lipopolysaccharide
- Listerien
- Makrophage
- Makrosomie
- Malignes Melanom
- Manie
- MAP1LC3B
- Massive parallele Sequenzierung
- Melatonin
- Menachinon
- Mendelsche Randomisierung
- Mesolimbisches System
- Metabolit
- Metagenomik
- Migräne
- Mikrobiom
- Mikroglia
- Mikroorganismus
- Milchsäurebakterien
- Mineralstoff
- Miso
- Mitochondrium
- Mittelhirn
- Modellorganismus
- Molke
- Monozyt
- Morbus Crohn
- mRNA
- mTOR
- Mukosa
- Multiple Sklerose
- Myelin
- N-Acetyltaurin
- N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid
- Nattō
- Nekroptose
- Nekrose
- Neotam
- Nervensystem
- Nervenzelle
- Nervus Vagus
- Neuralrohrdefekt
- Neurogenese
- Neuronale Plastizität
- Neuropeptide
- Neurotransmitter
- NF-κB
- Nicotinamid
- Nicotinamidadenindinukleotid
- NKT-Zelle
- Non-Profit-Organisation
- Notch-Signalweg
- Nucleus accumbens
- Nutrigenomik
- Olivenöl
- Omics
- Oncom
- Open Access
- Organoid
- Organoschwefelverbindungen
- Orientierung
- Oxidativer Stress
- Papillomaviridae
- Paracetamol
- Parkinson-Krankheit
- PD-1
- Peptostreptococcus
- Peyer-Plaques
- Pflanzenfresser
- Phenylmilchsäure
- Phosphorylierung
- Phylum
- Pilze
- Plasmid
- Pleiotropie
- Porphyromonadaceae
- Präfrontaler Cortex
- Prevotellaceae
- Probiotikum
- Progenitorzelle
- Prokaryoten
- Propionibakterien
- Propionsäure
- Protein
- Proteobacteria
- Psychedelikum
- Reaktive Sauerstoffspezies
- Reanimation
- Regulatorische T-Zellen
- Reizdarmsyndrom
- Relativität
- Replikation
- Response Element
- Ribosomale RNA
- RNA-Interferenz
- RNA-Virus
- Ruminococcus
- Saccharin
- Salutogenese
- SARS-CoV-2
- Sauerkraut
- Sauerteig
- SCFAs
- Schlaf
- Schlafentzug
- Schmalz
- Schuppenflechte
- Schwangerschaftsdiabetes
- Schwefelwasserstoff
- Senolytika
- Serotonin
- Sevofluran
- Sirolimus
- SOD1
- Sonnenblumenöl
- Soziale Isolation
- Speisesalz
- Spektroskopie
- Spiegelneuron
- Spinat
- Stammzelle
- Staphylokokken
- Steatohepatitis
- Stevia
- Stress
- Striatum
- Stuhltransplantation
- Substanz P
- Succinate
- Sucralose
- Süßstoffe
- Süßwasserpolypen
- Sympathikus
- Synbiotikum
- Systematische Übersichtsarbeit
- T-Lymphozyt
- T-Zell-Rezeptor
- Tachykinine
- Taurin
- Telomer
- Tempeh
- Tetrahydrocannabinol
- TMPRSS2
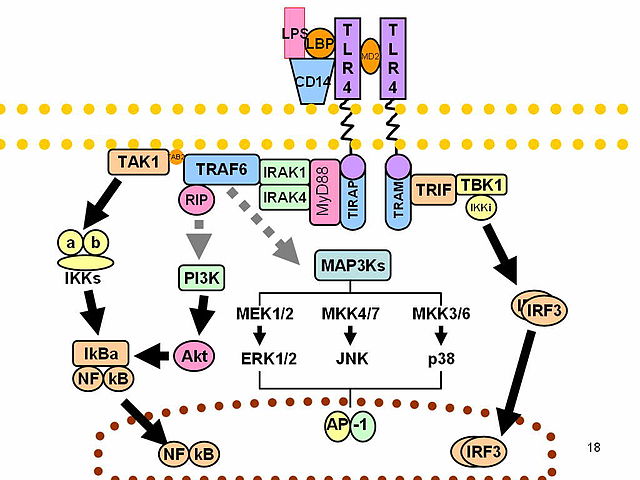
- Toll-like Receptor
- Toll-like-Rezeptor 5
- Tooltip-Informationen
- Tran
- Trans-Fettsäuren
- Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1
- Transkriptom
- Translation
- Translationale Medizin
- Tsukemono
- Tumornekrosefaktor
- Übergewicht
- Veganismus
- Vegetarismus
- Viren
- Vitamin
- Vitamin D
- Wasserstoff in der Biologie
- X-Chromosom
- Zellkultur
- Zellproliferation
- Zellteilung
- ZKBS
- Zöliakie
- Zucker
- Zytokin
Eine Auswahl der häufigsten Schlagworte/Tags. Die Vielzahl der Tags dient hier dazu, die Relevanz der „verwandten Beiträge“ zu verbessern.
Info-Krümel
Quellen und Tiefen
- 1HautinForm. Das Magazin aus der Hautarztpraxis. Berufsverband der Deutschen Dermatologen e. V. (uptoderm.de (Memento des Originals vom 16. Dezember 2013 im Internet Archive) 3-2013, S. 8.
- 2Eintrag zu Prebiotika. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, abgerufen am 23. Februar 2012.
- 3
- 4Senok, Abiola C; Verstraelen, Hans; Temmerman, Marleen; Botta, Giuseppe A; Senok, Abiola C (2009). "Probiotics for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4): CD006289. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006289.pub2. PMID 19821358.
- 5Mader JT, Calhoun J (1996). Baron S, et al. (eds.). Bone, Joint, and Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections. In: Baron's Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). Univ of Texas Medical Branch. ISBN 0-9631172-1-1.
- 6R. C. Hider, E. B. Fern, D. R. London: Relationship between intracellular amino acids and protein synthesis in the extensor digitorum longus muscle of rats. In: Biochem J 114, 1969, S. 171–178; PMID 5822066; PMC 1184841 (freier Volltext).
- 7E. Jówko, P. Ostaszewski, M. Jank, J. Sacharuk, A. Zieniewicz, J. Wilczak, S. Nissen: Creatine and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate (HMB) additively increase lean body mass and muscle strength during a weight-training program. In: Nutr 17, 2001, S. 558–566; doi:10.1016/S0899-9007(01)00540-8; PMID 11448573.
- 8Brook I. Anaerobic Infections. In: Diagnosis and Management. 4th Edition. New York: Informa Healthcare USA Inc.; 2007.
- 9Brook I. Recovery of anaerobic bacteria from clinical specimens in 12 years at two military hospitals. J Clin Microbiol. Jun 1988;26(6)1181-8.
- 10D. M. O’Connor und M. J. Crowe: Effects of beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate and creatine monohydrate supplementation on the aerobic and anaerobic capacity of highly trained athletes. In: J Sports Med Phys Fitness 43, 2003, S. 64–68; PMID 12629464.
- 11T. Palisin und J. J. Stacy: Beta-hydroxy-beta-Methylbutyrate and its use in athletics. In: Curr Sports Med Rep 4, 2005, S. 220–223; PMID 16004832.
- 12G. Slater, D. Jenkins, P. Logan, H. Lee, M. Vukovich, J. A. Rathmacher, A. G. Hahn: Beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB) supplementation does not affect changes in strength or body composition during resistance training in trained men. In: Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 11, 2001, S. 384–396, PMID 11599506.
- 13J. H. Baxter, J. L. Carlos, J. Thurmond, R. N. Rehani, J. Bultman, D. Frost: Dietary toxicity of calcium beta-hydroxy-beta-methyl butyrate (CaHMB). In: Food Chem Toxicol 43, 2005, S. 1731–1741; PMID 16006030.
- 14Lee, Mi Kyung; Choi, Soon Ho; Ryu, Dae Woong (2013-10-11). "Descending necrotizing Mediastinitis caused by Kocuria rosea: A case report". BMC Infectious Diseases. 13 (1): 475. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-13-475. ISSN 1471-2334. PMC 3852562. PMID 24112281.
- 15H. J. Smith, P. Mukerji, M. J. Tisdale: Attenuation of proteasome-induced proteolysis in skeletal muscle by beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate in cancerinduced muscle loss. In: Cancer Res 65
- 16Savini, V.; Catavitello, C.; Masciarelli, G.; Astolfi, D.; Balbinot, A.; Bianco, A.; Febbo, F.; D'Amario, C.; D'Antonio, D. (2010-09-30). "Drug sensitivity and clinical impact of members of the genus Kocuria". Journal of Medical Microbiology. 59 (12): 1395–1402. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.009-0. ISSN 0022-2615. PMID 20884772.
- 17H. L. Eley, S. T. Russell, M. J. Tisdale: Attenuation of depression of muscle protein synthesis induced by lipopolysaccharide, tumor necrosis factor, and angiotensin II by beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate. In: Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 295, 2008, S. E1409–1416; PMID 18854427.
- 18Karl Clauß und Harald Jensen (1973): Oxathiazinondioxide, eine neue Gruppe von Süßstoffen. In: Angewandte Chemie. Bd. 85, Nr. 22, S. 965–973. doi:10.1002/ange.19730852202.
- 19Waszkiewicz-Robak, B. (Szkola Glowna Gospodarstwa Wiejskiego, Warszawa (Poland). Wydzial Zywienia Czlowieka), Swiderski, F.: Some functional properties of highly intensive sweeteners. In: Przemysl Spozywczy (Poland). 1. Januar 2000 (fao.org [abgerufen am 9. Mai 2016]).
- 20Artikel Joghurt ohne Zuckerzusatz auf www.lebensmittelklarheit.de
- 21Registerauskunft für Registernummer 1004466 (Wortmarke „Sunett“), Deutsches Marken- und Patenamt, Stand 3. Februar 2013.
- 22Bundesinstitut für Risikobewertung: Bewertung von Süßstoffen und Zuckeraustauschstoffen. (PDF-Datei) Hintergrundinformation Nr. 025/2014 des BfR vom 1. Juli 2014, abgerufen am 30. November 2015.
- 23Sandro Castronovo, Arne Wick, Marco Scheurer, Karsten Nödler, Manoj Schulz, Thomas A. Ternes: Biodegradation of the artificial sweetener acesulfame in biological wastewater treatment and sandfilters. In: Water Research. 2016, doi:10.1016/j.watres.2016.11.041.
- 24Deutschlandfunk, Forschung Aktuell, Sendung vom 22. September 2011 Acesulfam: Unbehelligt durch Klo, Kanal und Kläranlage.
- 25Sandro Castronovo, Arne Wick, Marco Scheurer, Karsten Nödler, Manoj Schulz, Thomas A. Ternes: Biodegradation of the artificial sweetener acesulfame in biological wastewater treatment and sandfilters. In: Water Research. 2016, doi:10.1016/j.watres.2016.11.041.
- 26Robert Loos, Raquel Carvalho, Diana C. Antonio, Sara Comero, Giovanni Locoro, Simona Tavazzi, Bruno Paracchini, Michela Ghiani, Teresa Lettieri, Ludek Blaha, Barbora Jarosova, Stefan Voorspoels, Kelly Servaes, Peter Haglund, Jerker Fick, Richard H. Lindberg, David Schwesig, Bernd M. Gawlik: EU-wide monitoring survey on emerging polar organic contaminants in wastewater treatment plant effluents. In: Water Research. 2013. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2013.08.024.
- 27Andreas Fath: Rheines Wasser – 1231 Kilometer mit dem Strom, Carl Hanser Verlag, München 2016, ISBN 978-3-446-44871-1, S. 135–142.
- 28Andri Bryner: Flüsse sauber halten ist Vorsorge fürs Trinkwasser. In: eawag.ch, 9. September 2014, abgerufen am 15. März 2020.
- 29
- 30Shyjan AM, Bertagnolli M, Kenney CJ, Briskin MJ (April 1996). "Human mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1) demonstrates structural and functional similarities to the alpha 4 beta 7-integrin binding domains of murine MAdCAM-1, but extreme divergence of mucin-like sequences". Journal of Immunology. 156 (8): 2851–7. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.156.8.2851. PMID 8609404. S2CID 24940438.
- 31
- 32
- 33Bevilacqua MP (1993-04-01). "Endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecules". Annual Review of Immunology. 11 (1): 767–804. doi:10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.004003. PMID 8476577.
- 34Punt J (2019). Kuby immunology. Sharon A. Stranford, Patricia P. Jones, Judith A. Owen (Eighth ed.). New York. ISBN 978-1-4641-8978-4. OCLC 1002672752.
- 35Addressin Archived 2016-12-01 at the Wayback Machine at eMedicine Dictionary
- 36Berg EL, Robinson MK, Warnock RA, Butcher EC (July 1991). "The human peripheral lymph node vascular addressin is a ligand for LECAM-1, the peripheral lymph node homing receptor". The Journal of Cell Biology. 114 (2): 343–9. doi:10.1083/jcb.114.2.343. PMC 2289069. PMID 1712790.
- 37Bevilacqua MP (1993-04-01). "Endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecules". Annual Review of Immunology. 11 (1): 767–804. doi:10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.004003. PMID 8476577.
- 38Punt J (2019). Kuby immunology. Sharon A. Stranford, Patricia P. Jones, Judith A. Owen (Eighth ed.). New York. ISBN 978-1-4641-8978-4. OCLC 1002672752.
- 39Picker LJ, Butcher EC (1992-04-01). "Physiological and molecular mechanisms of lymphocyte homing". Annual Review of Immunology. 10 (1): 561–91. doi:10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.003021. PMID 1590996.
- 40Berg EL, Robinson MK, Warnock RA, Butcher EC (July 1991). "The human peripheral lymph node vascular addressin is a ligand for LECAM-1, the peripheral lymph node homing receptor". The Journal of Cell Biology. 114 (2): 343–9. doi:10.1083/jcb.114.2.343. PMC 2289069. PMID 1712790.
- 41Lechleitner S, Kunstfeld R, Messeritsch-Fanta C, Wolff K, Petzelbauer P (September 1999). "Peripheral lymph node addressins are expressed on skin endothelial cells". The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 113 (3): 410–4. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00696.x. PMID 10469342.
- 42Lechleitner S, Kunstfeld R, Messeritsch-Fanta C, Wolff K, Petzelbauer P (September 1999). "Peripheral lymph node addressins are expressed on skin endothelial cells". The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 113 (3): 410–4. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00696.x. PMID 10469342.
- 43Lechleitner S, Kunstfeld R, Messeritsch-Fanta C, Wolff K, Petzelbauer P (September 1999). "Peripheral lymph node addressins are expressed on skin endothelial cells". The Journal of Investigative Dermatology. 113 (3): 410–4. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00696.x. PMID 10469342.
- 44Arihiro S, Ohtani H, Suzuki M, Murata M, Ejima C, Oki M, et al. (2002). "Differential expression of mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1) in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease". Pathology International. 52 (5–6): 367–74. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1827.2002.01365.x. PMID 12100519. S2CID 38219521.
- 45
- 46R. Lüllmann-Rauch: Taschenlehrbuch Histologie 3. Auflage, Thieme, 2009, ISBN 978-3-13-129243-8.
- 47M. J. Lentze, K. Heyne: Pädiatrie: Grundlagen und Praxis. 2. Ausgabe, Springer, 2003, ISBN 3-540-43628-6, S. 215. eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche.
- 48Kirsty L. Spalding, Erik Arner, Pål O. Westermark, Samuel Bernard, Bruce A. Buchholz, Olaf Bergmann, Lennart Blomqvist, Johan Hoffstedt, Erik Naeslund, Tom Britton, Hernan Concha, Moustapha Hassan, Mikael Ryden, Jonas Frisen, Peter Arner: Dynamics of fat cell turnover in humans. In: Nature. 453, 2008, S. 783–787, doi:10.1038/nature06902. Siehe auch: Das Beharrungsvermögen der Adipozyten oder warum alle Diäten versagen. (Memento des vom 27. Juni 2013 im Internet Archive)
- 49Nabors, Lyn O’Brien: Alternative sweeteners. 4. Auflage. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL 2012, ISBN 1-4398-4615-4 (englisch, eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- 50Yusuke Amino, Kenich Mori, Yasuyuki Tomiyama, Hiroyuki Sakata, Takeshi Fujieda: Development of New, Low Calorie Sweetener: New Aspartame Derivative. In: Sweetness and Sweeteners. Band 979. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC 2008, ISBN 978-0-8412-7432-7, S. 463–480, doi:10.1021/bk-2008-0979.ch030 (englisch).
- 51Physics: past, present, future. In: Physics World: Policy and Funding Feature. Abgerufen am 31. Juli 2023.
- 52Markus Pössel: Von E=mc² zur Atombombe. (Memento vom 30. April 2008 im Internet Archive). Auf: einstein-online.info vom Max-Planck-Institut für Gravitationsphysik.
- 53Vgl. Albert Einstein: Why Socialism? In: John F. Sitton: Marx Today – Selected Works and Recent Debates. New York 2010, S. 171–175.
- 54Berufsverband Deutscher Internisten e. V., Allergie. Abgerufen am 24. Februar 2016.
- 55Herausgeber: Volker Friebel, Autoren: Ilse Ledvina, Armin Roßmeier So arbeitet das Immunsystem 1. Auflage, Falken-Verlag GmbH, Niederhausen/Ts. 1992, S. 51–58, ISBN 3-8068-1253-5.
- 56Renate Wahrig-Burfeind (Hrsg.): Wahrig. Illustriertes Wörterbuch der deutschen Sprache. ADAC-Verlag, München 2004, ISBN 3-577-10051-6, S. 623.
- 57Renate Wahrig-Burfeind (Hrsg.): Wahrig. Illustriertes Wörterbuch der deutschen Sprache. ADAC-Verlag, München 2004, ISBN 3-577-10051-6, S. 633.
- 58Matthias Schaefer: Wörterbuch der Ökologie. 4. Auflage, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg, Berlin 2003. ISBN 3-8274-0167-4, S. 215.
- 59Matthias Schaefer: Wörterbuch der Ökologie. 4. Auflage, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg, Berlin 2003. ISBN 3-8274-0167-4, S. 248.
- 60Rüdiger Wehner, Walter Gehring: Zoologie. 22. Auflage, Thieme, Stuttgart 1990, ISBN 3-13-367422-6, S. 268.
- 61Nentwig, Bacher, Beierkuhnlein, Brandl, Grabherr: Ökologie. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2004. ISBN 3-8274-0172-0, S. 143 f.
- 62Matthias Schaefer: Wörterbuch der Ökologie. 4. Auflage, Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg, Berlin 2003. ISBN 3-8274-0167-4, S. 248.
- 63Nentwig, Bacher, Beierkuhnlein, Brandl, Grabherr: Ökologie. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2004. ISBN 3-8274-0172-0, S. 143 f.
- 64Nentwig, Bacher, Beierkuhnlein, Brandl, Grabherr: Ökologie. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg 2004. ISBN 3-8274-0172-0, S. 143 f.
- 65C. P. Ferri et al.: Global prevalence of dementia: a Delphi consensus study. In: Lancet, Band 366, Nr. 9503, Dezember 2005, S. 2112–2117, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67889-0. PMID 16360788. PMC 2850264 (freier Volltext).
- 66Elisabeth Stechl, Catarina Knüvener et al.: Praxishandbuch Demenz. Erkennen - Verstehen - Behandeln. Mabuse-Verlag, Frankfurt am Main 2012, ISBN 978-3-86321-038-0.
- 67R. Mahlberg, H. Gutzmann (Hrsg.): Demenzerkrankungen erkennen, behandeln und versorgen. Deutscher Ärzte-Verlag, Köln 2009, ISBN 978-3-7691-0563-6.
- 68Sabine Engel: Alzheimer und Demenzen. Unterstützung für Angehörige. Trias-Verlag, Stuttgart 2012, ISBN 978-3-8304-3983-7.
- 69R. Mahlberg, H. Gutzmann (Hrsg.): Demenzerkrankungen erkennen, behandeln und versorgen. Deutscher Ärzte-Verlag, Köln 2012, ISBN 978-3-7691-0563-6.
- 70Skript (Memento vom 21. September 2008 im Internet Archive) (PDF; 612 kB) der Sendung Quarks & Co zum Thema Alzheimer
- 71Alexandra Bröhm: Warum Frauen häufiger an Alzheimer erkranken. In: welt.de. Axel Springer SE, 31. Mai 2016, abgerufen am 30. Dezember 2019
- 72Jane Gilmore: A possible 'link’ between menopause and Alzheimer’s is scaring women, including me. In: The Sydney Morning Herald. 7. Juni 2019, abgerufen am 30. Dezember 2019 (englisch).
- 73Deutsche Alzheimer Gesellschaft e. V.: Die Häufigkeit von Demenzerkrankungen. (PDF) Infoblatt 1. In: deutsche-alzheimer.de. Juni 2018, abgerufen am 9. August 2019.
- 74World Alzheimer Report 2015. The Global Impact of Dementia. (PDF) An analysis of prevalence, Incidence, cost and trends. Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI), August 2015, abgerufen am 9. August 2019 (englisch).
- 75D. Kapl, K. A. Rudolphi: Neue pharmakologische Aspekte zum neurologischen Profil von Propentofyllin. In: Tierärztliche Praxis (26)(K), 1998, S. 317–321
- 76"Die Ursachen der Alzheimer-Krankheit sind bislang nicht vollständig geklärt. Die bisherige Forschung zeigt, dass an ihrer Entstehung mehrere Faktoren beteiligt sind." In: Elisabeth Stechl, Catarina Knüvener et al.: Praxishandbuch Demenz. Erkennen - Verstehen - Behandeln. Mabuse-Verlag, Frankfurt am Main 2012, ISBN 978-3-86321-038-0., S. 192
- 77"Obgleich die Ätiologie der Alzheimer-Demenz letztlich weiterhin als ungeklärt bezeichnet werden muss, gab es doch in den letzten Jahren einen deutlichen Wissenszuwachs in der Pathologie der Erkrankung, in erster Linie auf der Basis von genetischen und molekularbiologischen Untersuchungen." In: R. Mahlberg, H. Gutzmann (Hrsg.): Demenzerkrankungen erkennen, behandeln und versorgen. Deutscher Ärzte-Verlag, Köln 2009, ISBN 978-3-7691-0563-6., S. 11 f.
- 78J. J. Iliff et al.: Impairment of glymphatic pathway function promotes tau pathology after traumatic brain injury. In: The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. Band 34, Nr. 49, Dezember 2014, S. 16180–16193, doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3020-14.2014, PMID 25471560, PMC 4252540 (freier Volltext).
- 79J. M. Tarasoff-Conway et al.: Clearance systems in the brain-implications for Alzheimer disease. In: Nature reviews. Neurology. Band 11, Nr. 8, August 2015, S. 457–470, doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2015.119, PMID 26195256, PMC 4694579 (freier Volltext) (Review).
- 80J. J. Iliff et al.: Impairment of glymphatic pathway function promotes tau pathology after traumatic brain injury. In: The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. Band 34, Nr. 49, Dezember 2014, S. 16180–16193, doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3020-14.2014, PMID 25471560, PMC 4252540 (freier Volltext).
- 81
- 82T. Jonsson et al.: A mutation in APP protects against Alzheimer’s disease and age-related cognitive decline. In: Nature. Band 488, Nr. 7409, August 2012, S. 96–99, doi:10.1038/nature11283. PMID 22801501.
- 83E. Rogaeva et al.: The neuronal sortilin-related receptor SORL1 is genetically associated with Alzheimer disease. In: Nature genetics. Band 39, Nr. 2, Februar 2007, S. 168–177, doi:10.1038/ng1943. PMID 17220890. PMC 2657343 (freier Volltext).
- 84F. Lopera et al.: Clinical features of early-onset Alzheimer disease in a large kindred with an E280A presenilin-1 mutation. In: JAMA. Band 277, Nr. 10, März 1997, S. 793–799, PMID 9052708.
- 85Pam Belluck: Alzheimer’s Stalks a Colombian Family. In: nytimes.com. 1. Juni 2010, abgerufen am 27. Juli 2015 (englisch).
- 86PSEN1 E280A (Paisa). In: alzforum.org. Abgerufen am 27. Juli 2015 (englisch).
- 87Andreas Kleinschmidt: Alzheimer Früherkennung. In: siemens.com. 15. April 2013, abgerufen am 27. Juli 2015.
- 88. Panza et al.: Amyloid-based immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease in the time of prevention trials: the way forward. In: Expert review of clinical immunology. Band 10, Nr. 3, März 2014, S. 405–419, doi:10.1586/1744666X.2014.883921, PMID 24490853 (Review).
- 89F. Panza et al.: Is there still any hope for amyloid-based immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease? In: Current opinion in psychiatry. Band 27, Nr. 2, März 2014, S. 128–137, doi:10.1097/YCO.0000000000000041, PMID 24445401 (Review).
- 90
- 91Klinische Studie (Phase I): A Multiple Ascending Dose Study of COR388 bei Clinicaltrials.gov der NIH
- 92S. J. Soscia et al.: The Alzheimer’s disease-associated amyloid beta-protein is an antimicrobial peptide. In: PloS one. Band 5, Nr. 3, 2010, S. e9505, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009505. PMID 20209079. PMC 2831066 (freier Volltext).
- 93Stephen S. Dominy et al.: Porphyromonas gingivalis in Alzheimer’s disease brains: Evidence for disease causation and treatment with small-molecule inhibitors In: Science Advances. Band 5, Nr. 1, 2019,
- 94
- 95Klinische Studie (Phase I): A Multiple Ascending Dose Study of COR388 bei Clinicaltrials.gov der NIH
- 96Michiyo Iba, Jing L. Guo, Jennifer D. McBride, Bin Zhang, John Q. Trojanowski und Virginia M.-Y. Lee: Synthetic Tau Fibrils Mediate Transmission of Neurofibrillary Tangles in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s-Like Tauopathy In: The Journal of Neuroscience. Nr. 33, 16. Januar 2013, S. 1024–1037.
- 97R. Mayeux, R. Ottman, M. Tang, L. Noboa-Bauza, K. Marder, B. Gurland, Y. Stern: Genetic susceptibility and head injury as risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease among community-dwelling elderly persons and their first-degree relatives. In: Ann Neurol. Band 33, Nr. 5, 1993, S. 494–501, PMID 8498827.
- 98K. F. Neumann, L. Rojo, L. P. Navarrete, G. Farías, P. Reyes, R. B. Maccioni: Insulin resistance and Alzheimer’s disease: molecular links & clinical implications. In: Curr Alzheimer Res.:. Nr. 5 (5), Oktober 2008, S. 438–447, PMID 18855585.
- 99J. S. Roriz-Filho, T. M. Sá-Roriz, I. Rosset, A. L. Camozzato, A. C. Santos, M. L. Chaves, J. C. Moriguti, M. Roriz-Cruz: (Pre)diabetes, brain aging, and cognition. In: Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009, S. 432–443, PMID 19135149.
- 100W. Q. Qiu, M. F. Folstein: Insulin, insulin-degrading enzyme and amyloid-beta peptide in Alzheimer’s disease: review and hypothesis. In: Neurobiol Aging. Feb; 27 (2), 2006, S. 190–198, PMID 19135149.
- 101O. S. Kofman, V. H. Macmillan: Diffuse cerebral atrophy. In: Applied therapeutics. Band 12, Nr. 4, April 1970, S. 24–26, PMID 5446326.
- 102M. Crisby, L. Carlson, B. Winblad: Statins in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer disease. In: Alzheimer Disease & Associated Disorders. Band 16, Nr. 3, 2002, S. 131–136, PMID 12218642.
- 103P. Kehoe, G. Wilcock: Is inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system a new treatment option for Alzheimer’s disease? In: Lancet neurology. Band 6, Nr. 4, 2007, S. 373–378, PMID 17362841.
- 104„Why stroke ups Alzheimer’s risk“ BBC, vom 4. Juni 2007
- 105Nigel Hawkes: Alzheimers linked to aluminium pollution in tap water. In: The Times. 20. April 2006, abgerufen am 7. April 2010.
- 106Virginie Rondeau, Daniel Commenges, Hélène Jacqmin-Gadda, Jean-François Dartigues: Relation between Aluminum Concentrations in Drinking Water and Alzheimer’s Disease: An 8-year Follow-up Study. In: Am J Epidemiology. 2000, PMID 10901330 (Online).
- 107V. Rondeau, H. Jacqmin-Gadda, D. Commenges, C. Helmer, J.-F. Dartigues: Aluminum and Silica in Drinking Water and the Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease or Cognitive Decline: Findings From 15-Year Follow-up of the PAQUID Cohort. In: American Journal of Epidemiology. Band 169, Nr. 4, 2008, S. 489–496, doi:10.1093/aje/kwn348, PMID 19064650, PMC 2809081 (freier Volltext).
- 108Sakae Yumoto, Shigeo Kakimi, Akihiro Ohsaki, Akira Ishikawa: Demonstration of aluminum in amyloid fibers in the cores of senile plaques in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. In: Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry. Band 103, Nr. 11, 2009, S. 1579–84, doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2009.07.023, PMID 19744735.
- 109P. C. Ferreira, A. Piai Kde, A. M. Takayanagui, S. I. Segura-Muñoz: Aluminum as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. In: Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. Band 16, Nr. 1, 2008, S. 151–157, doi:10.1590/S0104-11692008000100023, PMID 18392545 (Online).
- 110Alzheimer’s Society: Aluminium and Alzheimer’s disease. (PDF) In: The Learning Exchange. Juni 2002, abgerufen am 9. August 2019 (englisch).
- 111Bundesinstituts für Risikobewertung: Keine Alzheimer-Gefahr durch Aluminium aus Bedarfsgegenständen (PDF; 8 Seiten, 65 kB), am 4. Oktober 2013.
- 112Bundesinstitut für Risikobewertung: Aluminiumhaltige Antitranspirantien tragen zur Aufnahme von Aluminium bei. (PDF; 15 Seiten), am 10. März 2014
- 113Lilian Calderón-Garcidueñas et al.: Hallmarks of Alzheimer disease are evolving relentlessly in Metropolitan Mexico City infants, children and young adults. APOE4 carriers have higher suicide risk and higher odds of reaching NFT stage V at ≤ 40 years of age. In: Environmental Research, 164, 2018, S. 475, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2018.03.023.
- 114Hirnleistungs-Check zur Früherkennung einer Demenz. IGeL-Monitor; abgerufen am 15. Januar 2019. Wichtigste Quellen darin: Meta-Analyse Tsoi 2016. – KK Tsoi, HW Hirai, JY Chan, TC. Kwok: Time to Treatment Initiation in People With Alzheimer Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. In: Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 2016, 17, S. 24–30, PMID 26392193; sowie Systematisches Review Lin et al. 2013 – J. S. Lin, E. O’Connor, R. C. Rossom, L. A. Perdue, E. Eckstrom: Screening for cognitive impairment in older adults: A systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. In: Annals of internal medicine, 2013, 159, S. 601–612, PMID 24354019. Mehr zur Begründung der Bewertung in Evidenz kompakt. (PDF) abgerufen am 15. Januar 2019.
- 115AWMF: S3-Leitlinie "Demenzen". Abgerufen am 7. Januar 2021.
- 116MRT zur Früherkennung einer Alzheimer-Demenz. IGeL-Monitor; abgerufen am 15. Januar 2019. Wichtigste Quellen darin: NICE-Leitlinie von 2011. (National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence der britischen Gesundheitsbehörde NHS) sowie Meta-Analyse Schmand et al. 2010. – B. Schmand, H. M. Huizenga, W. A. van Gool: Meta-analysis of CSF and MRI biomarkers for detecting preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. In: Psychological Medicine, Januar 2010, 40 (1): S. 135–145, PMID 19863841. Mehr zur Begründung der Bewertung in der Evidenzsynthese. (PDF) abgerufen am 15. Januar 2019.
- 117Artikel aus dem Tagesspiegel. vom 21. Februar 2018 oder aus der Ärzte-Zeitung. vom 5. Dezember 2017.
- 118G. B. Frisoni et al.: Revised criteria for Alzheimer’s disease: what are the lessons for clinicians? In: The Lancet. Neurology. Band 10, Nr. 7, Juli 2011, S. 598–601, doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70126-0. PMID 21683925.
- 1197 Stufen von Alzheimer | Deutschland. Abgerufen am 15. April 2021.
- 120R. T. Linn et al.: The 'preclinical phase' of probable Alzheimer’s disease. A 13-year prospective study of the Framingham cohort. In: Arch Neurol. Band 52, Nr. 5, 1995, S. 485–490, PMID 7733843.
- 121J. Saxton et al.: Preclinical Alzheimer disease: neuropsychological test performance 1.5 to 8 years prior to onset. In: Neurology. Band 63, Nr. 12, 2004, S. 2341–2347, PMID 15623697.
- 122E. W. Twamley, S. A. Ropacki, M. W. Bondi: Neuropsychological and neuroimaging changes in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. In: J Int Neuropsychol Soc. Band 12, Nr. 5, 2006, S. 707–735, doi:10.1017/S1355617706060863, PMID 16961952.
- 123G. B. Frisoni et al.: Revised criteria for Alzheimer’s disease: what are the lessons for clinicians? In: The Lancet. Neurology. Band 10, Nr. 7, Juli 2011, S. 598–601, doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70126-0. PMID 21683925.
- 124G. B. Frisoni et al.: Revised criteria for Alzheimer’s disease: what are the lessons for clinicians? In: The Lancet. Neurology. Band 10, Nr. 7, Juli 2011, S. 598–601, doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70126-0. PMID 21683925.
- 125R. A. Sperling et al.: Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. In: Alzheimer’s & dementia. Band 7, Nr. 3, Mai 2011, S. 280–292, doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.003. PMID 21514248. PMC 3220946 freier Volltext.
- 126M. S. Albert et al.: The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. In: Alzheimer’s & dementia: the journal of the Alzheimer’s Association. Band 7, Nr. 3, Mai 2011, S. 270–279, doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.008. PMID 21514249. PMC 3312027 (freier Volltext).
- 127G. M. McKhann et al.: The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. In: Alzheimer’s & dementia: the journal of the Alzheimer’s Association. Band 7, Nr. 3, Mai 2011, S. 263–269, doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005. PMID 21514250. PMC 3312024 (freier Volltext).
- 128H.-J. Gertz, A. Kurz: Diagnose ohne Therapie. Frühdiagnostik der Alzheimer-Krankheit im Stadium der leichten kognitiven Beeinträchtigung. In: Der Nervenarzt. Band 82, Nr. 9, 2011, doi:10.1007/s00115-010-3213-3
- 129H. Barthel et al.: Cerebral amyloid-β PET with florbetaben (18F) in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and healthy controls: a multicentre phase 2 diagnostic study. In: The Lancet. Neurology. Band 10, Nr. 5, Mai 2011, S. 424–435, doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70077-1. PMID 21481640.
- 130Nutzenbewertung von Arzneimitteln mit neuen Wirkstoffen nach § 35a SGB V – Florbetaben, Beschluss des G-BA "neue Untersuchungsmethode" vom 20. Februar 2014, abgerufen am 6. März 2014
- 131Thomas Hauser et al..: Mild cognitive impairment. Diagnostische Wertigkeit verschiedener MRT-Techniken. In: Der Radiologe. 2011; 51: S. 285–292 doi:10.1007/s00117-010-2094-6
- 132Marcus Bauser, Lutz Lehmann: Positronen-Emissions-Tomographie. In: Chemie in unserer Zeit. Band 46, Nr. 2, 2012, S. 94, doi:10.1002/ciuz.201200564.
- 133M. S. Albert et al.: The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. In: Alzheimer’s & dementia: the journal of the Alzheimer’s Association. Band 7, Nr. 3, Mai 2011, S. 270–279, doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.008. PMID 21514249. PMC 3312027 (freier Volltext).
- 134L. Mucke: Neuroscience: Alzheimer’s disease. In: Nature. Band 461, 2009, S. 895–897, PMID 19829367.
- 135H. Förstl, A. Kurz: Clinical features of Alzheimer’s disease. In: European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience. Band 249, Nr. 6, 1999, S. 288–290, PMID 10653284.
- 136G. A. Carlesimo, M. Oscar-Berman: Memory deficits in Alzheimer’s patients: a comprehensive review. In: Neuropsychology Review. Band 3, Nr. 2, 1992, S. 119–169, PMID 1300219.
- 137M. Jelicic, A. E. Bonebakker, B. Bonke: Implicit memory performance of patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a brief review. In: International psychogeriatrics / IPA. Band 7, Nr. 3, 1995, S. 385–392, PMID 8821346.
- 138E. M. Frank: Effect of Alzheimer’s disease on communication function. In: Journal of the South Carolina Medical Association (1975). Band 90, Nr. 9, 1994, S. 417–423, PMID 7967534.
- 139J. T. Becker, A. A. Overman: [The semantic memory deficit in Alzheimer’s disease]. In: Revista De Neurologia. Band 35, Nr. 8, 2002, S. 777–783, PMID 12402233.
- 140J. R. Hodges, K. Patterson: Is semantic memory consistently impaired early in the course of Alzheimer’s disease? Neuroanatomical and diagnostic implications. In: Neuropsychologia. Band 33, Nr. 4, 1995, S. 441–459, PMID 7617154.
- 141T. Benke: Two forms of apraxia in Alzheimer’s disease. In: Cortex; a Journal Devoted to the Study of the Nervous System and Behavior. Band 29, Nr. 4, 1993, S. 715–725, PMID 8124945.
- 142H. Förstl, A. Kurz: Clinical features of Alzheimer’s disease. In: European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience. Band 249, Nr. 6, 1999, S. 288–290, PMID 10653284.
- 143Liz Kumru: Getting Lost in Alzheimer’s. UNMC; abgerufen am 22. Juli 2007 unmc.edu (Memento vom 10. Mai 2001 im Internet Archive)
- 144Tom Rickey: Road Skills Hint At “Motion Blindness” Of Alzheimer’s. University of Rochester Medical Center, 31. Januar 2002, abgerufen am 25. März 2016.
- 145Konzepte für Alzheimer-Impfungen im Testlabor. In: Deutsches Ärzteblatt. 9. November 2017, abgerufen am 9. August 2019.
- 146Antikörper löst Amyloid bei Alzheimer-Patienten.Ärzte Zeitung, 21. Mai 2010, abgerufen am 6. November 2010.
- 147rme/aerzteblatt.de: Alzheimer: Zweite Studie zur Antikörpertherapie abgebrochen. In: aerzteblatt.de. 7. August 2012, abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2014.
- 148Oliver Wirths et al.: Identification of low molecular weight pyroglutamate A{beta} oligomers in Alzheimer disease: a novel tool for therapy and diagnosis. In: The Journal of Biological Chemistry. Band 285, Nr. 53, 2010, S. 41517–41524, doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.178707, PMID 20971852, PMC 3009878 (freier Volltext)..
- 149Stefan Weller: Therapie gegen Alzheimer: Göttinger Forscher entwickeln neuen Ansatz für passive Immunisierung. Universitätsmedizin Göttingen - Georg-August-Universität, Pressemitteilung vom 5. November 2010 beim Informationsdienst Wissenschaft (idw-online.de), abgerufen am 6. November 2010.
- 150Gary W. Small: What we need to know about age related memory loss. In: British Medical Journal. 22. Juni 2002, abgerufen am 5. November 2006.
- 151M. Z. Scalco, R. van Reekum: Prevention of Alzheimer disease. Encouraging evidence. In: Canadian family physician Médecin de famille canadien. Band 52, Februar 2006, S. 200–207, PMID 16529393. PMC 1479722 (freier Volltext). (Review).
- 152Sam Norton et al.: Potential for primary prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: an analysis of population-based data. In: The Lancet Neurology. Band 13, Nr. 8, 2014, S. 788–794, doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70136-X (Online).
- 153K. A. Ginis et al.: Formulation of evidence-based messages to promote the use of physical activity to prevent and manage Alzheimer’s disease. In: BMC Public Health. Band 17, Nr. 1, Februar 2017, S. 209, doi:10.1186/s12889-017-4090-5, PMID 28212648, PMC 5316179 (freier Volltext).
- 154Äpfel fürs Hirn. Auf: wissenschaft.de vom 19. November 2004.
- 155Mit Fischöl gegen das Vergessen. Auf: wissenschaft.de vom 2. September 2004.
- 156M. Morris, J. Schneider, C. Tangney: Thoughts on B-vitamins and dementia. In: J Alzheimers Dis. Band 9, Nr. 4, 2006, S. 429–433, PMID 16917152.
- 157Inna I. Kruman et al.: Folic Acid Deficiency and Homocysteine Impair DNA Repair in Hippocampal Neurons and Sensitize Them to Amyloid Toxicity in Experimental Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. In: The Journal of Neuroscience. Band 22, Nr. 5, 1. März 2002, PMID 11880504. Einen vereinfachten Bericht findet man hier: www.alzheimers.org.uk
- 158Folate May Lower Alzheimer’s Risk In: CBS news, reporting from WebMD.
- 159NIH Press Release: Folic Acid Possibly A Key Factor In Alzheimer’s Disease Prevention. (Nicht mehr online verfügbar.) In: nih.gov. 3. Januar 2002, archiviert vom Original am 24. Juni 2014; abgerufen am 29. Dezember 2019.
- 160Kathleen Fackelmann: USATODAY.com - Folate shows promise in preventing Alzheimer’s. In: usatoday.com. 14. August 2005, abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2014.
- 161Raucher-Ausrede widerlegt. Auf: wissenschaft.de vom 8. Februar 2005.
- 162D. E. Zylberstein et al.: Midlife homocysteine and late-life dementia in women. A prospective population study. In: Neurobiology of aging. Band 32, Nr. 3, März 2011, S. 380–386, doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.02.024. PMID 19342123.
- 163A. D. Smith et al.: Homocysteine-lowering by B vitamins slows the rate of accelerated brain atrophy in mild cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial. In: PloS one. Band 5, Nr. 9, 2010, S. e12244, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012244. PMID 20838622. PMC 2935890 (freier Volltext).
- 164G. Douaud et al.: Preventing Alzheimer’s disease-related gray matter atrophy by B-vitamin treatment. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Band 110, Nr. 23, Juni 2013, S. 9523–9528, doi:10.1073/pnas.1301816110. PMID 23690582. PMC 3677457 (freier Volltext).
- 165Die Wunderwaffe gegen Alzheimer. In: vitamin-b12-mangel.org. Juli 2013, abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2014.
- 166Andrea Gerlin: Vitamins That Cost Pennies a Day Seen Delaying Dementia - Businessweek. In: businessweek.com. 20. Mai 2013, abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2014.
- 167Education May Not Protect Against Dementia as Previously Thought. Rush University, 6. Februar 2019, abgerufen am 9. August 2019 (englisch).
- 168Roy Eccleston: Think or sink. (PDF) (Nicht mehr online verfügbar.) In: The Weekend Australian Magazine. 2. Dezember 2006, archiviert vom Original am 23. Juli 2008; abgerufen am 3. Januar 2009.
- 169Kreuzworträtsel lösen reicht nicht. (Nicht mehr online verfügbar.) In: GesundheitPro.de. 8. November 2007, archiviert vom Original am 10. Juli 2009; abgerufen am 3. Januar 2009.
- 170Blutdruck senkende Mittel können Demenz vorbeugen. wissenschaft.de, 14. Oktober 2002.
- 171A. Brüning: Wie Cholesterin das Risiko für Alzheimer erhöht. In: Berliner Zeitung, 11. Oktober 2005.
- 172Berliner Zeitung, 24. Oktober 2013, S. 12.
- 173J. P. Guo, S. Yu, PL. McGeer: Simple in vitro assays to identify amyloid-beta aggregation blockers for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. In: J Alzheimers Dis. Band 19, Nr. 4, 2010, S. 1359–1370, PMID 20061605.
- 174S, Abbas, M. Mink: Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits beta amyloid oligomerization in Caenorhabditis elegans and affects the daf-2/insulin-like signaling pathway. In: J Alzheimers Dis. Band 17, Nr. 11, 2010, S. 902–909, PMID 20382008.
- 175D. E. Ehrnhoefer et al.: EGCG redirects amyloidogenic polypeptides into unstructured, off-pathway oligomers. In: Nat Struct Mol Biol. Band 15, Nr. 5, Juni 2008, S. 558–566, PMID 18511942.
- 176J. Bieschke et al.: EGCG remodels mature α-synuclein and amyloid-β fibrils and reduces cellular toxicity. In: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. Band 107, Nr. 17, April 2010, PMID 20385841.
- 177F. Meng et al.: The flavanol (–)-epigallocatechin 3-gallate inhibits amyloid formation by islet amyloid polypeptide, disaggregates amyloid fibrils, and protects cultured cells against IAPP-induced toxicity. In: Biochemistry. Band 49, Nr. 37, September 2010, PMID 20707388.
- 178K. Rezai-Zadeh et al.: Green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) reduces beta-amyloid mediated cognitive impairment and modulates tau pathology in Alzheimer transgenic mice. In: Brain Res. Band 12, Nr. 1214, Juni 2008, S. 177–186, PMID 18457818.
- 179
- 180G. Grelle et al.: Black Tea Theaflavins Inhibit Formation of Toxic Amyloid-β and α-Synuclein Fibrils. In: Biochemistry. November 2011, PMID 22054421.
- 181P. E. Cramer et al.: ApoE-directed therapeutics rapidly clear β-amyloid and reverse deficits in AD mouse models. In: Science. Band 335, Nr. 6075, März 2012, S. 1503–1506, doi:10.1126/science.1217697. PMID 22323736. PMC 3651582 (freier Volltext).
- 182Jessica Studeny: Drug quickly reverses Alzheimer’s symptoms in mice. Veröffentlichung der Case Western Reserve University, 9. Februar 2012.
- 183Drug Quickly Reverses Alzheimer’s Symptoms in Mice. Meldung bei Neurosciencenews.com vom 10. Februar 2012.
- 184Harald Frater: Krebsmedikament macht Alzheimer-Symptome rückgängig: Wirkstoff Bexaroten beseitigt Gedächtnisstörungen und Eiweiß-Plaques bei Mäusen. In: g-o.de. 10. Februar 2012, abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2014.
- 185E. O’Hare et al.: Lack of support for bexarotene as a treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. In: Neuropharmacology. [elektronische Veröffentlichung vor dem Druck] Mai 2015, doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.04.020, PMID 26025659.
- 186C. Balducci et al.: The Continuing Failure of Bexarotene in Alzheimer’s Disease Mice. In: Journal of Alzheimer’s disease: JAD. [elektronische Veröffentlichung vor dem Druck] März 2015, doi:10.3233/JAD-150029, PMID 25777514.
- 187B. Tousi: The emerging role of bexarotene in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: current evidence. In: Neuropsychiatric disease and treatment. Band 11, 2015, S. 311–315, doi:10.2147/NDT.S61309, PMID 25709453, PMC 4327563 (freier Volltext) (Review).
- 188Weblink für Paper Paul T. Francis, Gordon K. Wilcock et al.: The cholinergic hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: a review of progress In: J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry (1999)
- 189Huperzine A Alzheimer Research Forum
- 190B. S. Wang, H. Wang, Z. H. Wei, Y. Y. Song, L. Zhang, H. Z. Chen: Efficacy and safety of natural acetylcholinesterase inhibitor huperzine A in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: an updated meta-analysis. In: Journal of Neural Transmission. Band 116, Nr. 4, 2009, S. 457–465, doi:10.1007/s00702-009-0189-x, PMID 19221692.
- 191B. Winblad, J. Cummings, N. Andreasen et al.: A six-month double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of a transdermal patch in Alzheimer’s disease – rivastigmine patch versus capsule. In: International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, Band 22, Nr. 5, S. 456–467, May 2007 doi:10.1002/gps.1788 PMID 17380489
- 192H. Kaduszkiewicz, T. Zimmermann, H. P. Beck-Bornholdt, Hendrik van den Bussche: Cholinesterase inhibitors for patients with Alzheimer’s disease: systematic review of randomised clinical trials. In: BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.). Band 331, Nr. 7512, August 2005, S. 321–327, PMID 16081444, PMC 1183129 (freier Volltext).
- 193T. Lempert, T. Bschor: [Treatment of Alzheimer’s disease according to the S3 guidelines on dementia. Choline esterase inhibitors for all and for ever?]. In: Der Nervenarzt. Band 82, Nr. 1, Januar 2011, S. 90–91, doi:10.1007/s00115-010-3233-z. PMID 21274696.
- 194J. C. Breitner, K. A. Welsh et al.: Delayed onset of Alzheimer’s disease with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory and histamine H2 blocking drugs. In: Neurobiology of Aging Volume 16, Issue 4, Pages 523-530, July 1995 PMID 8544901
- 195T. Wyss-Coray, L. Mucke: Ibuprofen, inflammation and Alzheimer disease. In: Nature medicine. Band 6, Nr. 9, September 2000, S. 973–974, doi:10.1038/79661. PMID 10973311.
- 196D. Dokmeci: Ibuprofen and Alzheimer’s disease. In: Folia medica. Band 46, Nr. 2, 2004, S. 5–10, PMID 15506544. (Review).
- 197T. Morihara et al.: Ibuprofen suppresses interleukin-1beta induction of pro-amyloidogenic alpha1-antichymotrypsin to ameliorate beta-amyloid (Abeta) pathology in Alzheimer’s models. In: Neuropsychopharmacology: official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology. Band 30, Nr. 6, Juni 2005, S. 1111–1120, doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1300668. PMID 15688088.
- 198A. C. McKee et al.: Ibuprofen reduces Abeta, hyperphosphorylated tau and memory deficits in Alzheimer mice. In: Brain research. Band 1207, Mai 2008, S. 225–236, doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.01.095. PMID 18374906. PMC 2587244 (freier Volltext).
- 199M. Sastre et al.: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs repress beta-secretase gene promoter activity by the activation of PPARgamma. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Band 103, Nr. 2, Januar 2006, S. 443–448, doi:10.1073/pnas.0503839103. PMID 16407166. PMC 1326151 (freier Volltext)./mfn] Beim Menschen liegen bisher keine Daten aus randomisierten Doppelblind-Studien vor, die eine gesicherte Wirkungsweise von Ibuprofen und anderen nichtsteroidalen Antirheumatika aufzeigen. Aufgrund der nicht unerheblichen Nebenwirkungen, die bei einer dauerhaften prophylaktischen Einnahme von Ibuprofen zu erwarten sind, wird von einer unkontrollierten Einnahme abgeraten.199N. Tabet, H. Feldmand: Ibuprofen for Alzheimer’s disease. In: The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. Nr. 2, 2003, S. CD004031, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004031. PMID 12804498. (Review).
- 200B. De Strooper, G. König: An inflammatory drug prospect. In: Nature. Band 414, Nr. 6860, November 2001, S. 159–160, doi:10.1038/35102656. PMID 11700538.
- 201Gregor Larbig: Studien zur Identifizierung & Optimierung potentieller Wirkstoffe für die Behandlung von Morbus Alzheimer. Dissertation, TU Darmstadt, 2007
- 202T. Müller: Neue Wege gegen das Amyloid im Hirn. In: Ärzte Zeitung am 7. Dezember 2007
- 203M. Krohn et al.: Cerebral amyloid-β proteostasis is regulated by the membrane transport protein ABCC1 in mice. In: The Journal of clinical investigation. Band 121, Nr. 10, Oktober 2011, S. 3924–3931, doi:10.1172/JCI57867. PMID 21881209. PMC 3195473 (freier Volltext).
- 204R. McShane, A. Areosa Sastre, N. Minakaran: Memantine for dementia. In: The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. Nr. 2, 2006, S. CD003154, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003154.pub5. PMID 16625572. (Review).
- 205J. Birks, Evans J. Grimley: Ginkgo biloba for cognitive impairment and dementia. In: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. Nr. 2, 2007, S. CD003120, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003120.pub2, PMID 17443523
- 206J. Birks, E. Grimley, M. Van Dongen: Ginkgo biloba for cognitive impairment and dementia. In: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. S. CD003120, PMID 12519586.
- 207S. T. DeKosky, A. Fitzpatrick, D. G. Ives, J. Saxton, J. Williamson, O. L. Lopez, G. Burke, L. Fried, L. H. Kuller, J. Robbins, R. Tracy, N. Woolard, L. Dunn, R. Kronmal, R. Nahin, C. Furberg: The Ginkgo Evaluation of Memory (GEM) study: design and baseline data of a randomized trial of Ginkgo biloba extract in prevention of dementia. In: Contemp Clin Trials. Band 27, Nr. 3, 2006, S. 238–253, doi:10.1016/j.cct.2006.02.007, PMID 16627007.
- 208Ginkgo Biloba Does Not Reduce Dementia Risk, Study Shows. In: sciencedaily.com. 19. November 2008, abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2014.
- 209B. E. Snitz et al.: Ginkgo biloba for preventing cognitive decline in older adults: a randomized trial. In: JAMA. Band 302, Nr. 24, Dezember 2009, S. 2663–2670, doi:10.1001/jama.2009.1913. PMID 20040554. PMC 2832285 (freier Volltext).
- 210Stefan Weinmann et al.: Effects of Ginkgo biloba in dementia: systematic review and meta-analysis. In: BMC Geriatrics 2010, 10:14 doi:10.1186/1471-2318-10-14
- 211
- 212B. Kastenholz: Phytopharmaceuticals in the therapy of younger Alzheimer patients. WebmedCentral AGING 2011; 2 (7): WMC002011.
- 213S. Krishnan, R. Cairns, R. Howard: Cannabinoids for the treatment of dementia. In: The Cochrane database of systematic reviews. Nr. 2, 2009, S. CD007204, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007204.pub2, PMID 19370677 (Review).
- 214S. Craft et al.: Intranasal insulin therapy for Alzheimer disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a pilot clinical trial. In: Archives of neurology. Band 69, Nr. 1, Januar 2012, S. 29–38, doi:10.1001/archneurol.2011.233. PMID 21911655. PMC 3260944 (freier Volltext).
- 215M. W. Dysken et al.: Effect of vitamin E and memantine on functional decline in Alzheimer disease: the TEAM-AD VA cooperative randomized trial. In: JAMA. Band 311, Nr. 1, Januar 2014, S. 33–44, doi:10.1001/jama.2013.282834. PMID 24381967. PMC 4109898 (freier Volltext).
- 216M. Sano et al.: A controlled trial of selegiline, alpha-tocopherol, or both as treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. The Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study. In: The New England Journal of Medicine. Band 336, Nr. 17, April 1997, S. 1216–1222, doi:10.1056/NEJM199704243361704. PMID 9110909.
- 217R. C. Petersen et al.: Vitamin E and donepezil for the treatment of mild cognitive impairment. In: The New England Journal of Medicine. Band 352, Nr. 23, Juni 2005, S. 2379–2388, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa050151. PMID 15829527.
- 218J. H. Kang et al.: A randomized trial of vitamin E supplementation and cognitive function in women. In: Archives of internal medicine. Band 166, Nr. 22, 2006 Dec 11-25, S. 2462–2468, doi:10.1001/archinte.166.22.2462. PMID 17159011.
- 219J. H. Kang et al.: Vitamin E, vitamin C, beta carotene, and cognitive function among women with or at risk of cardiovascular disease: The Women’s Antioxidant and Cardiovascular Study. In: Circulation. Band 119, Nr. 21, Juni 2009, S. 2772–2780, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.816900. PMID 19451353. PMC 2752297 (freier Volltext).
- 220E. R. Miller et al.: Meta-analysis: high-dosage vitamin E supplementation may increase all-cause mortality. In: Annals of internal medicine. Band 142, Nr. 1, Januar 2005, S. 37–46, PMID 15537682.
- 221Hilkka Soininen et al.: 24-month intervention with a specific multinutrient in people with prodromal Alzheimer’s disease (LipiDiDiet): a randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. In: The Lancet Neurology. Band 0, Nr. 0, ISSN 1474-4422, doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30332-0 (Online ,abgerufen am 11. November 2017).
- 222Ärzte Zeitung: Europäische Studie: Hilft Nährstoff-Kombi bei Alzheimer im Frühstadium? Abgerufen am 11. November 2017.
- 223J. Cohen-Mansfield: Nonpharmacologic interventions for inappropriate behaviors in dementia: a review, summary, and critique. In: Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 9 (4), 2001, S. 361–381. PMID 11739063 (Review)
- 224
- 225L. E. Middleton et al.: Activity energy expenditure and incident cognitive impairment in older adults. In: Archives of internal medicine. Band 171, Nr. 14, Juli 2011, S. 1251–1257, doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2011.277. PMID 21771893. PMC 3923462 (freier Volltext).
- 226M. N. Vercambre et al.: Physical activity and cognition in women with vascular conditions. In: Archives of internal medicine. Band 171, Nr. 14, Juli 2011, S. 1244–1250, doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2011.282. PMID 21771894. PMC 3153432 (freier Volltext).
- 227T. E. Dunne, S. A. Neargarder, P. B. Cipolloni, A. Cronin-Golomb: Visual contrast enhances food and liquid intake in advanced Alzheimer’s disease. In: Clin Nutr. Band 23, Nr. 4, 2004, S. 533–538, PMID 15297089.
- 228S3-Leitlinie Demenzen. 2017, doi:10.1007/978-3-662-53875-3.
- 229A. Alzheimer: Über eine eigenartige Erkrankung der Hirnrinde. In: Allg. Z. Psychiat. Psych.-Gerichtl. Med. Band 64, Nr. 1–2, 1907, S. 146–148.
- 230Konrad Maurer, Ulrike Maurer: Alzheimer: the life of a physician and the career of a disease. Columbia University Press, New York 2003.
- 231Fred H. Hochberg, David Rottenberg: Neurological classics in modern translation. Hafner Press, New York 1977, ISBN 0-02-851180-8.
- 232N. C. Berchtold, C. W. Cotman: Evolution in the conceptualization of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: Greco-Roman period to the 1960s. In: Neurobiol. Aging. Band 19, Nr. 3, 1998, S. 173–189, PMID 9661992.
- 233Emil Kraepelin: Textbook of Psychiatry. 1910.
- 234M. B. Graeber et al.: Rediscovery of the case described by Alois Alzheimer in 1911: historical, histological and molecular genetic analysis. In: Neurogenetics. Band 1, Nr. 1, Mai 1997, S. 73–80, PMID 10735278.
- 235U. Müller, P. Winter, M. B. Graeber: A presenilin 1 mutation in the first case of Alzheimer’s disease. In: The Lancet. Neurology. Band 12, Nr. 2, Februar 2013, S. 129–130, doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70307-1. PMID 23246540.
- 236Preisgekrönte Filmbiographie Iris von 2001. Darin wird die Geschichte ihres Verfalls aus der Sicht ihres Mannes John Bayley beschrieben. Murdoch wurde von Kate Winslet und Judi Dench dargestellt.
- 237Jochen Wittmann: Pratchetts "Choosing to die: Selbstmord zur besten Sendezeit. In: derstandard.at. 15. Juni 2011, abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2014.
- 238Tilman Jens: Vaters Vergessen. In: FAZ.net. 4. März 2008, abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2014.
- 239Paul Wolff: Von der Leyen und die Krankheit ihres Vaters. In: welt.de. 27. Mai 2008, abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2014.
- 240Zum Beispiel Titelthema in Die Zeit, 12. Mai 2011: Die Angst vor Alzheimer
- 241Gabriel García Márquez: Literaturnobelpreisträger leidet an Demenz. In: Spiegel Online. 8. Juli 2012, abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2014.
- 242Bitter irony of Alzheimer’s for Nobel laureate Marquez as his symptoms mimic masterpiece.
- 243Gerd Müller wird 70. In: fcbayern.de. 6. Oktober 2015, abgerufen am 6. Oktober 2015.
- 244DHPV-Ehrenpreis an Arno Geiger auf www.dhpv.de, 10. Oktober 2011
- 245Aus dem Schatten treten – Warum ich mich für unsere Rechte als Demenzbetroffene einsetze von Helga Rohra auf www.demenz-support.de
- 246Ralph Trommer: Meister der leisen Töne. In: taz.de. 4. November 2013, abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2014.
- 247Michela Farabella: Italo, con te partirò. Hrsg.: Carello Edizioni. Turin 2019, ISBN 978-88-96864-81-4, S. 144.
- 248
- 249Interview mit Regisseurin Barbara Wachendorff. In: Sommerblut – Festival der Multipolarkultur. 7. Mai 2012, abgerufen am 9. August 2019.
- 250
- 251Eines Tages… Offizielle Homepage zum Spielfilm
- 252DVD-Box Demenz. In: LVR-Klinikverbund. Landschaftsverband Rheinland (LVR), abgerufen am 9. August 2019.
- 253Von Johan Dehoust: Maxim Gorki Theater: Stuhlkreis mit Kater. In: Spiegel Online. 2. Januar 2013, abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2014.
- 254Thomas Liesen (Buch und Regie), Ulrike Schweitzer (Redaktion): Leben, Lieben, Vergessen… Längengrad-Filmproduktion, 2013 Online bei YouTube.
- 255Filmdrama "Still Alice", Infos und Bewertung auf score11.de, abgerufen am 12. September 2015.
- 256
- 257Belastung der Gesundheitssysteme und der Volkswirtschaft durch Alzheimer (PDF) In: Medical Tribune, 36/2009
- 258Georg Löffler: Biochemie und Pathobiochemie. Springer-Verlag, 2013, ISBN 978-3-662-06062-9, S. 25.
- 259Katharina Munk (Hrsg.): Biochemie – Zellbiologie. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 2008, ISBN 978-3-13-144831-6, S. 122, Google Books.
- 260Peter Nuhn: Naturstoffchemie. S. Hirzel Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft, Stuttgart 1990, ISBN 3-7776-0473-9, S. 70.
- 261G. Genchi: An overview on D-amino acids. In: Amino Acids. Band 49, Nummer 9, September 2017, S. 1521–1533, doi:10.1007/s00726-017-2459-5. PMID 28681245.
- 262NASA Researchers Make First Discovery of Life’s Building Block in Comet. nasa.gov, August 2009; Chiral amino acids in meteorites strengthen evidence for extraterrestrial life. spie.org, September 2010 (abgerufen am 4. Oktober 2010).
- 263Parte, A.C. "Asaccharobacter". LPSN.
- 264"Asaccharobacter celatus". www.uniprot.org.
- 265https://www.uniprot.org/taxonomy/394340
- 266"Asaccharobacter celatus". www.uniprot.org.
- 267Minamida, K.; Ota, K.; Nishimukai, M.; Tanaka, M.; Abe, A.; Sone, T.; Tomita, F.; Hara, H.; Asano, K. (1 May 2008). "Asaccharobacter celatus gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from rat caecum". International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 58 (5): 1238–1240. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64894-0. PMID 18450720.
- 268Shekhar HU, Howlader ZH, Kabir Y (2016). Exploring the Nutrition and Health Benefits of Functional Foods. IGI Global. ISBN 978-1522505914.
- 269Fundamental beliefs about atherosclerosis overturned. Complications of artery-hardening condition are number one killer worldwide. In: ScienceDaily. Abgerufen am 26. Januar 2020 (englisch).
- 270The top 10 causes of death. In: www.who.int. Abgerufen am 26. Januar 2020 (englisch).
- 271Hans H. Lauer: Geschichtliches zur Koronarsklerose. BYK Gulden, Konstanz 1971 (Aus dem Institut für Geschichte der Medizin der Universität Heidelberg), S. 15–17.
- 272Glinda S Cooper, Berrit C Stroehla: The epidemiology of autoimmune diseases. In: Autoimmunity Reviews. Band 2, Nr. 3, Mai 2003, S. 119–125, doi:10.1016/S1568-9972(03)00006-5 (elsevier.com
- 273Lifeng Wang, Fu-Sheng Wang, M. Eric Gershwin: Human autoimmune diseases: a comprehensive update. In: Journal of Internal Medicine. Band 278, Nr. 4, Oktober 2015, S. 369–395, doi:10.1111/joim.12395 (wiley.com
- 274S.T. Ngo, F.J. Steyn, P.A. McCombe: Gender differences in autoimmune disease. In: Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology. Band 35, Nr. 3, August 2014, S. 347–369, doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2014.04.004 (elsevier.com
- 275Franz Hrska, Wolfgang Graninger, Michael Frass: Systemerkrankungen. In: Anästhesiologie Intensivmedizin Notfallmedizin Schmerztherapie. Band 38, Nr. 11, (November) 2003, S. 719–740, hier: S. 720 f.
- 276Institut für Medizinische Mikrobiologie, Immunologie und Parasitologie: Bacteriocine – Lantibiotika (Memento vom 11. November 2013 im Internet Archive), Universität Bonn.
- 277Richard F. Shand, Kathryn J. Leyva: Archaeal Antimicrobials: An undiscovered country. In: Paul Blum (Hrsg.): Archaea: New Models for Prokaryotic Biology. Caister Academic Press, 2008, ISBN 978-1-904455-27-1, S. 233f.
- 278H. Lee, H. Y. Kim: Lantibiotics, class I bacteriocins from the genus Bacillus. In: Journal of microbiology and biotechnology. Band 21, Nummer 3, März 2011, ISSN 1738-8872, S. 229–235. PMID 21464591.
- 279A. Gratia: Sur un remarquable exemple d'antagonisme entre deux souches de colibacille. In: Compt. Rend. Soc. Biol. Band 93, 1925, S. 1040–1042.
- 280J. P. Gratia: Andre Gratia: a forerunner in microbial and viral genetics. In: Genetics. Band 156, Nr. 2, 2000, S. 471–6. PMID 11014798. PMC 1461273 (freier Volltext)
- 281
- 282K. A. Stevens u. a.: Nisin treatment for inactivation of Salmonella species and other gram-negative bacteria. In: Applied and Environmental Microbiology. Band 57, Nr. 12, 1991, S. 3613–3615.
- 283E. Breukink, B. de Kruijff: The lantibiotic nisin, a special case or not? In: Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. Band 1462, Nummer 1–2, Dezember 1999, ISSN 0006-3002, S. 223–234. PMID 10590310.
- 284Eintrag zu Reutericyclin. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, abgerufen am 11. November 2013.
- 285Kathryn E Holt u. a.: Tracking the Establishment of Local Endemic Populations of an Emergent Enteric Pathogen. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 110.43, 2013, S. 17522–17527. doi:10.1073/pnas.1308632110.
- 286Ulrich Welsch: Lehrbuch Histologie. 2. Auflage. Urban & Fischer bei Elsevier, München 2006, ISBN 3-437-44430-1, S. 108.
- 287Herbert Lippert: Lehrbuch Anatomie. 7. Auflage. Urban & Fischer bei Elsevier, München 2006, ISBN 3-437-42362-2, S. 25 ff.
- 288Herbert Lippert: Lehrbuch Anatomie. 7. Auflage. Urban & Fischer bei Elsevier, München 2006, ISBN 3-437-42362-2, S. 25 ff.
- 289Ulrich Welsch: Lehrbuch Histologie. 2. Auflage. Urban & Fischer bei Elsevier, München 2006, ISBN 3-437-44430-1, S. 108.
- 290Norbert Ulfig: Kurzlehrbuch Histologie. 2. Auflage. Thieme, Stuttgart 2005, ISBN 3-13-135572-7, S. 44.
- 291Dietrich Frohne, Uwe Jensen: Systematik des Pflanzenreiches unter besonderer Berücksichtigung chemischer Merkmale und pflanzlicher Drogen, 4. Auflage, Gustav Fischer Verlag Stuttgart, Jena, New York, ISBN 3-437-20486-6, S. 313.
- 292Lea, Tor (2015). "Caco-2 Cell Line". The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: 103–111. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-16104-4_10.
- 293Lea, Tor (2015). "Caco-2 Cell Line". The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: 103–111. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-16104-4_10.
- 294Fogh, Jørgen; Fogh, Jens M.; Orfeo, Thomas (July 1977). "One Hundred and Twenty-Seven Cultured Human Tumor Cell Lines Producing Tumors in Nude Mice23". JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 59 (1): 221–226. doi:10.1093/jnci/59.1.221.
- 295"Absorption Systems". Archived from the original on 2010-05-29.
- 296Pinto M (1983). "Enterocyte-like differentiation and polarization of the human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2 in culture". Biol Cell. 47: 323–30.
- 297Hidalgo IJ, Raub TJ, Borchardt RT (March 1989). "Characterization of the human colon carcinoma cell line (Caco-2) as a model system for intestinal epithelial permeability". Gastroenterology. 96 (3): 736–49. doi:10.1016/0016-5085(89)90897-4. PMID 2914637.
- 298Sambuy Y, De Angelis I, Ranaldi G, Scarino ML, Stammati A, Zucco F (January 2005). "The Caco-2 cell line as a model of the intestinal barrier: influence of cell and culture-related factors on Caco-2 cell functional characteristics". Cell Biology and Toxicology. 21 (1): 1–26. doi:10.1007/s10565-005-0085-6. PMID 15868485. S2CID 125735.
- 299Nauli AM, Whittimore JD (August 2015). "Using Caco-2 Cells to Study Lipid Transport by the Intestine". Journal of Visualized Experiments (102): e53086. doi:10.3791/53086. PMC 4692536. PMID 26325673.
- 300Hidalgo IJ, Raub TJ, Borchardt RT (March 1989). "Characterization of the human colon carcinoma cell line (Caco-2) as a model system for intestinal epithelial permeability". Gastroenterology. 96 (3): 736–49. doi:10.1016/0016-5085(89)90897-4. PMID 2914637.
- 301Artursson P (June 1990). "Epithelial transport of drugs in cell culture. I: A model for studying the passive diffusion of drugs over intestinal absorptive (Caco-2) cells". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 79 (6): 476–82. doi:10.1002/jps.2600790604. PMID 1975619.
- 302Vázquez-Sánchez MÁ. "CacoReady". Readycell. Readycell. Retrieved 19 July 2018.
- 303Artursson P, Karlsson J (March 1991). "Correlation between oral drug absorption in humans and apparent drug permeability coefficients in human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 175 (3): 880–5. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(91)91647-U. PMID 1673839.
- 304Carl H. June, Michel Sadelain: Chimeric Antigen Receptor Therapy. In: New England Journal of Medicine, 2018, Band 379, Ausgabe 1, 5. Juli 2018, S. 64–73, doi:10.1056/NEJMra1706169
- 305CAR T Cells: Engineering Patients’ Immune Cells to Treat Their Cancers. Cancer.gov; abgerufen am 9. September 2017
- 306FDA approves Roche’s Actemra/RoActemra (tocilizumab) for the treatment of CAR T cell-induced cytokine release syndrome. Roche, Pressemitteilung vom 30. August 2017; abgerufen am 30. April 2022.
- 307Choe JH, Williams JZ, Lim WA, Engineering T Cells to Treat Cancer: The Convergence of Immuno-Oncology and Synthetic Biology, in: Annual Review of Cancer Biology 4 (2020) S. 121–139 doi=10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-030419-033657
- 308Definition of autologous iCASP9-CD19-expressing T lymphocytes. In: National Cancer Institute. Abgerufen am 2. Juli 2020.
- 309Porcelli S, Brenner MB, Greenstein JL, Balk SP, Terhorst C, Bleicher PA (1989). "Recognition of cluster of differentiation 1 antigens by human CD4-CD8-cytolytic T lymphocytes". Nature. 341 (6241): 447–50. doi:10.1038/341447a0. PMID 2477705..
- 310Zajonc DM, Wilson IA (2007). "Architecture of CD1 proteins". Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology. 314: 27–50. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-69511-0_2. ISBN 978-3-540-69510-3. PMID 17593656.
- 311Sköld M, Behar SM (2005). "The role of group 1 and group 2 CD1-restricted T cells in microbial immunity". Microbes Infect. 7(3): 544–51. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2004.12.012. PMID 15777730.
- 312Angenieux C, Salamero J, Fricker D, Cazenave JP, Goud B, Hanau D, de La Salle H (2000). "Characterization of CD1e, a third type of CD1 molecule expressed in dendritic cells". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (48): 37757–64. doi:10.1074/jbc.M007082200. PMID 10948205.
- 313Kumarasen C, Anthony S-Y L (2003). Manual of diagnostic antibodies for immunohistology. London: Greenwich Medical Media. pp. 59–60. ISBN 1-84110-100-1.
- 314Van Rhijn I, Koets AP, Im JS, Piebes D, Reddington F, Besra GS, Porcelli SA, van Eden W, Rutten VP (2006). "The bovine CD1 family contains group 1 CD1 proteins, but no functional CD1d". J. Immunol. 176 (8): 4888–93. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.176.8.4888. PMID 16585584.
- 315Gao G, Jakobsen B (2000). "Molecular interactions of coreceptor CD8 and MHC class I: the molecular basis for functional coordination with the T-cell receptor". Immunol Today. 21 (12): 630–6. doi:10.1016/S0167-5699(00)01750-3. PMID 11114424.
- 316Klaus D. Elgert: Immunology. John Wiley & Sons, 2009, ISBN 978-0-470-08157-0, S. 30.
- 317Kenneth M. Murphy, Paul Travers, Mark Walport: Janeway - Immunologie. Korrigierter Nachdruck 2014. 7. Auflage. Springer Spektrum, Berlin 2014, ISBN 978-3-662-44227-2.
- 318Leong, Anthony S-Y; Cooper, Kumarason; Leong, F Joel W-M: Manual of Diagnostic Cytology. 2. Auflage. Greenwich Medical Media, Ltd., 2003, ISBN 1-84110-100-1, S. 73.
- 319J. Fontaine, C. Bovens, S. Bettenay, R. S. Mueller: Canine cutaneous epitheliotropic T-cell lymphoma: a review. In: Veterinary and comparative oncology. Band 7, Nummer 1, März 2009, S. 1–14, doi:10.1111/j.1476-5829.2008.00176.x, PMID 19222826
- 320Abul K. Abbas: Cellular and Molecular Immunology. Elsevier Health Sciences, 2014, ISBN 978-0-323-28645-9, S. 147.
- 321William E. Paul: Fundamental Immunology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2012, ISBN 978-1-451-18203-3, S. 11.
- 322"anti-Human CD8" (PDF). Bangs Laboratories, Inc. 21 March 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-10-13. Retrieved 2016-08-18.
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326"CD8 alpha - Marker for cytotoxic T Lymphocytes". Archived from the original on 21 September 2015. Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- 327Martin Jinek, Krzysztof Chylinski, Ines Fonfara, Michael Hauer, Jennifer A. Doudna, Emmanuelle Charpentier: A Programmable Dual-RNA–Guided DNA Endonuclease in Adaptive Bacterial Immunity. In: Science. Band 337, Nr. 6096, 17. August 2012, ISSN 0036-8075, S. 816–821, doi:10.1126/science.1225829, PMID 22745249.
- 328H. Ochiai: Single-Base Pair Genome Editing in Human Cells by Using Site-Specific Endonucleases. In: International journal of molecular sciences. Band 16, Nummer 9, 2015, S. 21128–21137, doi:10.3390/ijms160921128, PMID 26404258, PMC 4613245 (freier Volltext) (Review).
- 329M. M. Mahfouz, A. Piatek, C. N. Stewart: Genome engineering via TALENs and CRISPR/Cas9 systems: challenges and perspectives. In: Plant biotechnology journal. Band 12, Nummer 8, Oktober 2014, S. 1006–1014, doi:10.1111/pbi.12256, PMID 25250853.
- 330E. Pennisi: The CRISPR craze. In: Science. Band 341, Nummer 6148, August 2013, S. 833–836, doi:10.1126/science.341.6148.833, PMID 23970676.
- 331Email Science: And Science’s Breakthrough of the Year is … In: news.sciencemag.org. 17. Dezember 2015, abgerufen am 17. Dezember 2015 (englisch).
- 332H. C. Douglas, S. E. Gunter: The taxonomic position of Corynebacterium acnes. In: Journal of bacteriology. Band 52, Juli 1946, S. 15–23, ISSN 0021-9193. PMID 20994865.
- 333Gunther Müller: Grundlagen der Lebensmittelmikrobiologie. 6. Auflage. Steinkopff Verlag, Darmstadt 1986, ISBN 3-7985-0673-6, S. 62.
- 334Gunther Müller: Grundlagen der Lebensmittelmikrobiologie. 6. Auflage. Steinkopff Verlag, Darmstadt 1986, ISBN 3-7985-0673-6, S. 62.
- 335Details: DSM-25643. In: www.dsmz.de.
- 336The structures of 7,4’-dihydroxy-isoflavan and its precursors is shown in Structural Elucidation of Hydroxylated Metabolites of the Isoflavan Equol by GC/MS and HPLC/MS by Corinna E. Rüfer, Hansruedi Glatt, and Sabine E. Kulling in Drug Metabolism and Disposition (2005, electronic publication).
- 337Wang XL, Hur HG, Lee JH, Kim KT, Kim SI (January 2005). "Enantioselective synthesis of S-equol from dihydrodaidzein by a newly isolated anaerobic human intestinal bacterium". Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71 (1): 214–9. Bibcode:2005ApEnM..71..214W. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.1.214-219.2005. PMC 544246. PMID 15640190.
- 338Muthyala, Rajeev S; Ju, Young H; Sheng, Shubin; Williams, Lee D; Doerge, Daniel R; Katzenellenbogen, Benita S; Helferich, William G; Katzenellenbogen, John A (2004). "Equol, a natural estrogenic metabolite from soy isoflavones". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 12 (6): 1559–1567. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2003.11.035. ISSN 0968-0896. PMID 15018930.
- 339Frankenfeld CL, Atkinson C, Thomas WK, et al. (December 2005). "High concordance of daidzein-metabolizing phenotypes in individuals measured 1 to 3 years apart". Br. J. Nutr. 94 (6): 873–6. doi:10.1079/bjn20051565. PMID 16351761.
- 340Marrian, GF; Haslewood, GA (1932). "Equol, a new inactive phenol isolated from the ketohydroxyoestrin fraction of mares' urine". The Biochemical Journal. 26 (4): 1227–32. doi:10.1042/bj0261227. PMC 1261026. PMID 16744928.
- 341Axelson, M; Kirk, DN; Farrant, RD; Cooley, G; Lawson, AM; Setchell, KD (1982-02-01). "The identification of the weak oestrogen equol [7-hydroxy-3-(4'-hydroxyphenyl)chroman] in human urine". The Biochemical Journal. 201 (2): 353–7. doi:10.1042/bj2010353. PMC 1163650. PMID 7082293.
- 342Setchell, KD; Clerici, C (July 2010). "Equol: history, chemistry, and formation". The Journal of Nutrition. 140 (7): 1355S–62S. doi:10.3945/jn.109.119776. PMC 2884333. PMID 20519412.
- 343Setchell, KD; Borriello, SP; Hulme, P; Kirk, DN; Axelson, M (September 1984). "Nonsteroidal estrogens of dietary origin: possible roles in hormone-dependent disease". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 40 (3): 569–78. doi:10.1093/ajcn/40.3.569. PMID 6383008. S2CID 4467689.
- 344Marrian, GF; Haslewood, GA (1932). "Equol, a new inactive phenol isolated from the ketohydroxyoestrin fraction of mares' urine". The Biochemical Journal. 26 (4): 1227–32. doi:10.1042/bj0261227. PMC 1261026. PMID 16744928.
- 345
- 346Wang XL, Hur HG, Lee JH, Kim KT, Kim SI (January 2005). "Enantioselective synthesis of S-equol from dihydrodaidzein by a newly isolated anaerobic human intestinal bacterium". Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71 (1): 214–9. Bibcode:2005ApEnM..71..214W. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.1.214-219.2005. PMC 544246. PMID 15640190.
- 347Mueller SO, Simon S, Chae K, Metzler M, Korach KS (April 2004). "Phytoestrogens and their human metabolites show distinct agonistic and antagonistic properties on estrogen receptor {α} (ER{α}) and ERβ in human cells". Toxicol. Sci. 80 (1): 14–25. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfh147. PMID 15084758.
- 348Muthyala, Rajeev S; Ju, Young H; Sheng, Shubin; Williams, Lee D; Doerge, Daniel R; Katzenellenbogen, Benita S; Helferich, William G; Katzenellenbogen, John A (2004). "Equol, a natural estrogenic metabolite from soy isoflavones". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 12 (6): 1559–1567. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2003.11.035. ISSN 0968-0896. PMID 15018930.
- 349Setchell, KD; Clerici, C; Lephart, ED; Cole, SJ; Heenan, C; Castellani, D; Wolfe, BE; Nechemias-Zimmer, L; Brown, NM; Lund, TD; Handa, RJ; Heubi, JE (May 2005). "S-equol, a potent ligand for estrogen receptor beta, is the exclusive enantiomeric form of the soy isoflavone metabolite produced by human intestinal bacterial flora". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 81 (5): 1072–9. doi:10.1093/ajcn/81.5.1072. PMID 15883431.
- 350Prossnitz, Eric R.; Barton, Matthias (2014). "Estrogen biology: New insights into GPER function and clinical opportunities". Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 389 (1–2): 71–83. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2014.02.002. ISSN 0303-7207. PMC 4040308. PMID 24530924.
- 351Setchell, KD; Zhao, X; Jha, P; Heubi, JE; Brown, NM (Oct 2009). "The pharmacokinetic behavior of the soy isoflavone metabolite S-(-)equol and its diastereoisomer R-(+)equol in healthy adults determined by using stable-isotope-labeled tracers". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 90 (4): 1029–37. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.27981. PMC 2744624. PMID 19710188.
- 352Setchell, KD; Zhao, X; Shoaf, SE; Ragland, K (Nov 2009). "The pharmacokinetics of S-(-)equol administered as SE5-OH tablets to healthy postmenopausal women". The Journal of Nutrition. 139 (11): 2037–43. doi:10.3945/jn.109.110874. PMID 19776178.
- 353Setchell, KD; Clerici, C (Jul 2010). "Equol: pharmacokinetics and biological actions". The Journal of Nutrition. 140 (7): 1363S–8S. doi:10.3945/jn.109.119784. PMC 2884334. PMID 20519411.
- 354Setchell, KD; Borriello, SP; Hulme, P; Kirk, DN; Axelson, M (September 1984). "Nonsteroidal estrogens of dietary origin: possible roles in hormone-dependent disease". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 40 (3): 569–78. doi:10.1093/ajcn/40.3.569. PMID 6383008. S2CID 4467689.
- 355Setchell, KD; Clerici, C (July 2010). "Equol: history, chemistry, and formation". The Journal of Nutrition. 140 (7): 1355S–62S. doi:10.3945/jn.109.119776. PMC 2884333. PMID 20519412.
- 356Setchell, KD; Clerici, C (July 2010). "Equol: history, chemistry, and formation". The Journal of Nutrition. 140 (7): 1355S–62S. doi:10.3945/jn.109.119776. PMC 2884333. PMID 20519412.
- 357Setchell, KD; Clerici, C (July 2010). "Equol: history, chemistry, and formation". The Journal of Nutrition. 140 (7): 1355S–62S. doi:10.3945/jn.109.119776. PMC 2884333. PMID 20519412.
- 358Setchell, KD; Cole, SJ (August 2006). "Method of defining equol-producer status and its frequency among vegetarians". The Journal of Nutrition. 136 (8): 2188–93. doi:10.1093/jn/136.8.2188. PMID 16857839.
- 359Rowland, IR; Wiseman, H; Sanders, TA; Adlercreutz, H; Bowey, EA (2000). "Interindividual variation in metabolism of soy isoflavones and lignans: influence of habitual diet on equol production by the gut microflora". Nutrition and Cancer. 36 (1): 27–32. doi:10.1207/S15327914NC3601_5. PMID 10798213. S2CID 10603402.
- 360Watanabe, S; Yamaguchi, M; Sobue, T; Takahashi, T; Miura, T; Arai, Y; Mazur, W; Wähälä, K; Adlercreutz, H (October 1998). "Pharmacokinetics of soybean isoflavones in plasma, urine and feces of men after ingestion of 60 g baked soybean powder (kinako)". The Journal of Nutrition. 128 (10): 1710–5. doi:10.1093/jn/128.10.1710. PMID 9772140.
- 361Arai, Y; Uehara, M; Sato, Y; Kimira, M; Eboshida, A; Adlercreutz, H; Watanabe, S (March 2000). "Comparison of isoflavones among dietary intake, plasma concentration and urinary excretion for accurate estimation of phytoestrogen intake". Journal of Epidemiology. 10 (2): 127–35. doi:10.2188/jea.10.127. PMID 10778038.
- 362Akaza, H; Miyanaga, N; Takashima, N; Naito, S; Hirao, Y; Tsukamoto, T; Fujioka, T; Mori, M; Kim, WJ; Song, JM; Pantuck, AJ (February 2004). "Comparisons of percent equol producers between prostate cancer patients and controls: case-controlled studies of isoflavones in Japanese, Korean and American residents". Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology. 34 (2): 86–9. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyh015. PMID 15067102.
- 363Song, KB; Atkinson, C; Frankenfeld, CL; Jokela, T; Wähälä, K; Thomas, WK; Lampe, JW (May 2006). "Prevalence of daidzein-metabolizing phenotypes differs between Caucasian and Korean American women and girls". The Journal of Nutrition. 136 (5): 1347–51. doi:10.1093/jn/136.5.1347. PMID 16614428.
- 364Patisaul, HB; Jefferson, W (October 2010). "The pros and cons of phytoestrogens". Front Neuroendocrinol. 31 (4): 400–419. doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2010.03.003. PMC 3074428. PMID 20347861.
- 365
- 366
- 367Setchell, KD; Cole, SJ (August 2006). "Method of defining equol-producer status and its frequency among vegetarians". The Journal of Nutrition. 136 (8): 2188–93. doi:10.1093/jn/136.8.2188. PMID 16857839.
- 368Setchell KD, Clerici C, Lephart ED, Cole SJ, Heenan C, Castellani D, Wolfe BE, Nechemias-Zimmer L, Brown NM, Lund TD, Handa RJ, Heubi JE (2005). "S-equol, a potent ligand for estrogen receptor beta, is the exclusive enantiomeric form of the soy isoflavone metabolite produced by human intestinal bacterial flora". Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 81 (5): 1072–9. doi:10.1093/ajcn/81.5.1072. PMID 15883431.
- 369Setchell, K. D.; Clerici, C. (2010). "Equol: History, Chemistry, and Formation". The Journal of Nutrition. 140 (7): 1355S–1362S. doi:10.3945/jn.109.119776. PMC 2884333. PMID 20519412.
- 370V, Ravishankar Rai; Bai, Jamuna A. (2014-12-17). Beneficial Microbes in Fermented and Functional Foods. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4822-0663-0.
- 371Reeve V, Widyarini S, Domanski D, Chew K, Barnes K. Protection Against Photoaging in the Hairless Mouse by the Isoflavone Equol. Photochemistry and Photobiology, Volume 81, Issue 6, November 2005, Pages 1548-1553
- 372Magnet, U.; Urbanek, C.; Gaisberger, D.; Tomeva, E.; Dum, E.; Pointner, A.; Haslberger, A.G. (October 2017). "Topical equol preparation improves structural and molecular skin parameters". International Journal of Cosmetic Science. 39 (5): 535–542. doi:10.1111/ics.12408. PMID 28574180. S2CID 44910993.
- 373Lephart ED (November 2016). "Skin aging and oxidative stress: Equol's anti-aging effects via biochemical and molecular mechanisms". Ageing Research Reviews. 31: 36–54. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2016.08.001. PMID 27521253. S2CID 205668316.
- 374Lephart ED (November 2016). "Skin aging and oxidative stress: Equol's anti-aging effects via biochemical and molecular mechanisms". Ageing Research Reviews. 31: 36–54. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2016.08.001. PMID 27521253. S2CID 205668316.
- 375Lephart, Edwin (2018-01-29). "Equol's Anti-Aging Effects Protect against Environmental Assaults by Increasing Skin Antioxidant Defense and ECM Proteins While Decreasing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation". Cosmetics. 5 (1): 16. doi:10.3390/cosmetics5010016. ISSN 2079-9284.
- 376Lephart, Edwin D. (November 2013). "Protective effects of equol and their polyphenolic isomers against dermal aging: Microarray/protein evidence with clinical implications and unique delivery into human skin". Pharmaceutical Biology. 51 (11): 1393–1400. doi:10.3109/13880209.2013.793720. ISSN 1388-0209. PMID 23862588.
- 377Lephart, Edwin D. (November 2013). "Protective effects of equol and their polyphenolic isomers against dermal aging: Microarray/protein evidence with clinical implications and unique delivery into human skin". Pharmaceutical Biology. 51 (11): 1393–1400. doi:10.3109/13880209.2013.793720. ISSN 1388-0209. PMID 23862588.
- 378Effect of natural S-equol on bone metabolism in equol non-producing postmenopausal Japanese women: a pilot randomized placebo-controlled trial. Tomomi Ueno of Saga Nutraceutricals Research Institute, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Japan, et.al
- 379Mayr, Linda; Georgiev, Dimitar; Toulev, Albena (2019-03-01). "Eine Proof-of-concept-Studie von Isoflavandiol-E55-RS-Vaginalkapseln oder Vaginalgel zur Linderung der menopausalen Vaginalatrophie". Journal für Gynäkologische Endokrinologie/Österreich (in German). 29 (1): 13–22. doi:10.1007/s41974-019-0085-9. ISSN 1996-1553.
- 380"Equol Is a Novel Anti-Androgen that Inhibits Prostate Growth and Hormone Feedback, Biology of Reproduction, Volume 70, Issue 4, 1 April 2004, Pages 1188–1195,". academic.oup.com. Retrieved 2023-11-17.
- 381Roman Büttner: Das Phänomen Fast Food. 2014, Google-Book-Vorschau, Seite 8
- 382Renate Lüllmann-Rauch: Histologie. Georg Thieme, Stuttgart 2009, ISBN 978-3-13-129243-8, S. 116–117.
- 383H. Knoche: Histologie und Histopathologie: Kurzlehrbuch für medizinisch-technische Assistenten. Springer, Berlin 2013, ISBN 978-3-642-67537-9, S. 47.
- 384Frans van den Berg: Physiologie. Band 1. Georg Thieme, Stuttgart 2003, ISBN 978-3-13-116032-4, S. 6–7.
- 385Martin Breitenseher: Bildgebende Diagnostik und Therapie der Weichteiltumoren. Mit pathologischer Klassifikation, Nuklearmedizin, interventioneller Therapie. Georg Thieme, Stuttgart 2008, ISBN 978-3-13-143131-8, S. 134.
- 386Noel R. Krieg u. a. (Hrsg.): Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. 2. Auflage. Band 4: The Bacteroidetes, Spirochaetes, Tenericutes (Mollicutes), Acidobacteria, Fibrobacteres, Fusobacteria, Dictyoglomi, Gemmatimonadetes, Lentisphaerae, Verrucomicrobia, Chlamydiae, and Planctomycetes. Springer, New York 2010, ISBN 978-0-387-68572-4.
- 387Jean P. Euzéby, Aidan C. Parte: Fusobacteria. In: List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN). Abgerufen am 24. November 2020.
- 388Stichwort mnestisch in: Brockhaus Enzyklopädie 2002 digital, bibliographisches Institut & F. A. Brockhaus AG, 2002
- 389Stichwort mnestisch in: Duden – das große Wörterbuch der deutschen Sprache, Dudenverlag, 2000; vergleiche auch die Angaben online unter dem Stichwort Amnesie unter „Herkunft“
- 390Wortgeschichte auf etymonline.com (englisch)
- 391Muller FL, Lustgarten MS, Jang Y, Richardson A, Van Remmen H (Aug 2007). "Trends in oxidative aging theories". Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 43 (4): 477–503. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.03.034. PMID 17640558.
- 392Esworthy RS, Aranda R, Martín MG, Doroshow JH, Binder SW, Chu FF (Sep 2001). "Mice with combined disruption of Gpx1 and Gpx2 genes have colitis". American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 281 (3): G848-55. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.2001.281.3.G848. PMID 11518697.
- 393Olson GE, Whitin JC, Hill KE, Winfrey VP, Motley AK, Austin LM, Deal J, Cohen HJ, Burk RF (May 2010). "Extracellular glutathione peroxidase (Gpx3) binds specifically to basement membranes of mouse renal cortex tubule cells". American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology. 298 (5): F1244-53. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00662.2009. PMC 2867408. PMID 20015939.
- 394Mills GC (Nov 1957). "Hemoglobin catabolism. I. Glutathione peroxidase, an erythrocyte enzyme which protects hemoglobin from oxidative breakdown". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 229 (1): 189–97. PMID 13491573.
- 395Zedan H, Abdel-Motaleb AA, Kassem NM, Hafeez HA, Hussein MR (Mar 2015). "Low glutathione peroxidase activity levels in patients with vitiligo". Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 19 (2): 144–8. doi:10.2310/7750.2014.14076. PMID 25775636.
- 396Yang S, Jensen MK, Rimm EB, Willett W, Wu T (Nov 2014). "Erythrocyte superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, and catalase activities and risk of coronary heart disease in generally healthy women: a prospective study". American Journal of Epidemiology. 180 (9): 901–8. doi:10.1093/aje/kwu195. PMC 4207716. PMID 25156995.
- 397Socha K, Kochanowicz J, Karpińska E, Soroczyńska J, Jakoniuk M, Mariak Z, Borawska MH (2014). "Dietary habits and selenium, glutathione peroxidase and total antioxidant status in the serum of patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis". Nutrition Journal. 13: 62. doi:10.1186/1475-2891-13-62. PMC 4080729. PMID 24943732.
- 398Katar M, Ozugurlu AF, Ozyurt H, Benli I (2014). "Evaluation of glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase enzyme polymorphisms in celiac disease patients". Genetics and Molecular Research. 13 (1): 1030–7. doi:10.4238/2014.February.20.4. PMID 24634124.
- 399Gnotobiotics. Schoeb, Trenton R.,, Eaton, Kathryn A. London. 11 August 2017. ISBN 978-0-12-804583-1. OCLC 1015915010.
- 400Vowles, Chriss J. (5 January 2016). Gnotobiotic mouse technology : an illustrated guide. Anderson, Natalie E.,, Eaton, Kathryn A. Boca Raton. ISBN 978-1-4987-3633-6. OCLC 924714283.
- 401Gnotobiotics. Schoeb, Trenton R.,, Eaton, Kathryn A. London. 11 August 2017. ISBN 978-0-12-804583-1. OCLC 1015915010.
- 402Vowles, Chriss J. (5 January 2016). Gnotobiotic mouse technology : an illustrated guide. Anderson, Natalie E.,, Eaton, Kathryn A. Boca Raton. ISBN 978-1-4987-3633-6. OCLC 924714283.
- 403Gnotobiotics. Schoeb, Trenton R.,, Eaton, Kathryn A. London. 11 August 2017. ISBN 978-0-12-804583-1. OCLC 1015915010.
- 404Vowles, Chriss J. (5 January 2016). Gnotobiotic mouse technology : an illustrated guide. Anderson, Natalie E.,, Eaton, Kathryn A. Boca Raton. ISBN 978-1-4987-3633-6. OCLC 924714283.
- 405Gnotobiotics. Schoeb, Trenton R.,, Eaton, Kathryn A. London. 11 August 2017. ISBN 978-0-12-804583-1. OCLC 1015915010.
- 406Williams, SCP (2014). "Gnotobiotics". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 111 (5): 1661. Bibcode: 2014PNAS..111.1661W. doi:10.1073/pnas.1324049111. PMC 3918800. PMID 24497491.
- 407Foster, John W.; Slonczewski, Joan L. (2009). Microbiology, An Evolving Science. W. W. Norton. p. 871. ISBN 978-0-393-93447-2.
- 408Foster, John W.; Slonczewski, Joan L. (2009). Microbiology, An Evolving Science. W. W. Norton. p. 871. ISBN 978-0-393-93447-2.
- 409Gnotobiotics. Schoeb, Trenton R.,, Eaton, Kathryn A. London. 11 August 2017. ISBN 978-0-12-804583-1. OCLC 1015915010.
- 410Zhang, Meiling; Shan, Chengjie; Tan, Fang; Limbu, Samwel Mchele; Chen, Liqiao; Du, Zhen-Yu (February 2020). "Gnotobiotic models: Powerful tools for deeply understanding intestinal microbiota-host interactions in aquaculture". Aquaculture. 517: 734800. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734800. ISSN 0044-8486.
- 411Gnotobiotics. Schoeb, Trenton R.,, Eaton, Kathryn A. London. 11 August 2017. ISBN 978-0-12-804583-1. OCLC 1015915010.
- 412Zhang, Meiling; Shan, Chengjie; Tan, Fang; Limbu, Samwel Mchele; Chen, Liqiao; Du, Zhen-Yu (February 2020). "Gnotobiotic models: Powerful tools for deeply understanding intestinal microbiota-host interactions in aquaculture". Aquaculture. 517: 734800. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734800. ISSN 0044-8486.
- 413W. Krienitz: Ueber das Auftreten von Spirochäten verschiedener Form im Mageninhalt bei Carcinoma ventriculi. In: Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. Band 32, 1906, S. 872.
- 414H. Kleinig, U. Maier: Kleinig/Sitte – Zellbiologie. 4. Auflage, Gustav-Fischer, 1999, ISBN 3-437-26010-3.
- 415J.T. Gallagher, M. Lyon: Proteoglycans: structure, biology and molecular interactions. Hrsg.: Iozzo, M, V. Marcel Dekker Inc. New York, New York, 2000, Molecular structure of Heparan Sulfate and interactions with growth factors and morphogens, S. 27–59.
- 416R. V. Iozzo: Matrix proteoglycans: from molecular design to cellular function. In: Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67. Jahrgang, 1998, S. 609–652, PMID 9759499.
- 417Wissenschaft-Online-Lexika: Eintrag zu Heparansulfat im Lexikon der Biologie.
- 418Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T, Hume DA: Interferon-gamma: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. In: J. Leukoc. Biol. 75. Jahrgang, Nr. 2, Februar 2004, S. 163–89, doi:10.1189/jlb.0603252, PMID 14525967.
- 419
- 420Schoenborn JR, Wilson CB: Regulation of interferon-gamma during innate and adaptive immune responses. In: Adv. Immunol. 96. Jahrgang, 2007, S. 41–101, doi:10.1016/S0065-2776(07)96002-2, PMID 17981204.
- 421Dumoutier L, Van Roost E, Colau D, Renauld JC (August 2000). "Human interleukin-10-related T cell-derived inducible factor: molecular cloning and functional characterization as an hepatocyte-stimulating factor". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 97 (18): 10144–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.170291697. PMC 27764. PMID 10954742.
- 422Xie MH, Aggarwal S, Ho WH, Foster J, Zhang Z, Stinson J, et al. (October 2000). "Interleukin (IL)-22, a novel human cytokine that signals through the interferon receptor-related proteins CRF2-4 and IL-22R". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (40): 31335–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005304200. PMID 10875937.
- 423PDB: 3DGC; Jones BC, Logsdon NJ, Walter MR (September 2008). "Structure of IL-22 bound to its high-affinity IL-22R1 chain". Structure. 16 (9): 1333–44. doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.06.005. PMC 2637415. PMID 18599299.
- 424Wolk K, Kunz S, Witte E, Friedrich M, Asadullah K, Sabat R (August 2004). "IL-22 increases the innate immunity of tissues". Immunity. 21 (2): 241–54. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2004.07.007. PMID 15308104.
- 425PDB: 3DGC; Jones BC, Logsdon NJ, Walter MR (September 2008). "Structure of IL-22 bound to its high-affinity IL-22R1 chain". Structure. 16 (9): 1333–44. doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.06.005. PMC 2637415. PMID 18599299.
- 426Dudakov JA, Hanash AM, van den Brink MR (2015-03-21). "Interleukin-22: immunobiology and pathology". Annual Review of Immunology. 33 (1): 747–85. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112123. PMC 4407497. PMID 25706098.
- 427Pan HF, Li XP, Zheng SG, Ye DQ (February 2013). "Emerging role of interleukin-22 in autoimmune diseases". Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews. 24 (1): 51–7. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2012.07.002. PMC 4003867. PMID 22906768.
- 428PDB: 3DGC; Jones BC, Logsdon NJ, Walter MR (September 2008). "Structure of IL-22 bound to its high-affinity IL-22R1 chain". Structure. 16 (9): 1333–44. doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.06.005. PMC 2637415. PMID 18599299.
- 429Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL, O'Garra A (2001). "Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor". Annual Review of Immunology. 19: 683–765. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.683. PMID 11244051..
- 430Sonnenberg GF, Nair MG, Kirn TJ, Zaph C, Fouser LA, Artis D (June 2010). "Pathological versus protective functions of IL-22 in airway inflammation are regulated by IL-17A". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 207 (6): 1293–305. doi:10.1084/jem.20092054. PMC 2882840. PMID 20498020.
- 431Dudakov JA, Hanash AM, van den Brink MR (2015-03-21). "Interleukin-22: immunobiology and pathology". Annual Review of Immunology. 33 (1): 747–85. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112123. PMC 4407497. PMID 25706098.
- 432Pestka S, Krause CD, Sarkar D, Walter MR, Shi Y, Fisher PB (2004). "Interleukin-10 and related cytokines and receptors". Annual Review of Immunology. 22: 929–79. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.22.012703.104622. PMID 15032600.
- 433Witte K, Witte E, Sabat R, Wolk K (August 2010). "IL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29: promising cytokines with type I interferon-like properties". Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews. 21 (4): 237–51. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2010.04.002. PMID 20655797.
- 434Xie MH, Aggarwal S, Ho WH, Foster J, Zhang Z, Stinson J, et al. (October 2000). "Interleukin (IL)-22, a novel human cytokine that signals through the interferon receptor-related proteins CRF2-4 and IL-22R". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (40): 31335–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005304200. PMID 10875937.
- 435Dudakov JA, Hanash AM, van den Brink MR (2015-03-21). "Interleukin-22: immunobiology and pathology". Annual Review of Immunology. 33 (1): 747–85. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112123. PMC 4407497. PMID 25706098.
- 436di Giovine FS, Duff GW (Jan 1990). „Interleukin 1: the first interleukin“. Immunology Today. 11 (1): 13–20. doi:10.1016/0167-5699(90)90005-t. PMID 2405873.
- 437Schindler R, Dinarello CA (1990). „Interleukin 1“. In Habenicht A (ed.). Growth Factors, Differentiation Factors, and Cytokines. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer. pp. 85–102. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-74856-1_7. ISBN 978-3-642-74856-1.
- 438„Revised nomenclature for antigen-nonspecific T cell proliferation and helper factors“. Journal of Immunology. 123 (6): 2928–9. Dec 1979. PMID 91646.
- 439Hopper AD, Hurlstone DP, Leeds JS, McAlindon ME, Dube AK, Stephenson TJ, Sanders DS (November 2006). "The occurrence of terminal ileal histological abnormalities in patients with coeliac disease". Digestive and Liver Disease. 38 (11): 815–819. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2006.04.003. PMID 16787773.
- 440DeFranco AL, Locksley RM, Robertson M (2007). The Immune Response in Infection and Inflammatory Disease. London: New Science Press. pp. 218–219. ISBN 978-0-19-920614-8.
- 441Olivares-Villagómez D, Van Kaer L (April 2018). "Intestinal Intraepithelial Lymphocytes: Sentinels of the Mucosal Barrier". Trends in Immunology. 39 (4): 264–275.
- 442McDonald BD, Jabri B, Bendelac A (August 2018). "Diverse developmental pathways of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes". Nature Reviews. Immunology. 18 (8): 514–525. doi:10.1038/s41577-018-0013-7. PMC 6063796. PMID 29717233.
- 443Sheridan BS, Lefrançois L (December 2010). "Intraepithelial lymphocytes: to serve and protect". Current Gastroenterology Reports. 12 (6): 513–521. doi:10.1007/s11894-010-0148-6. PMC 3224371. PMID 20890736.
- 444Mayassi T, Jabri B (September 2018). "Human intraepithelial lymphocytes". Mucosal Immunology. 11 (5): 1281–1289. doi:10.1038/s41385-018-0016-5. PMC 6178824. PMID 29674648.
- 445Lambolez F, Mayans S, Cheroutre H (2013). "Lymphocytes: Intraepithelial". eLS. American Cancer Society. doi:10.1002/9780470015902.a0001197.pub3. ISBN 9780470015902.
- 446Cheroutre H, Lambolez F (February 2008). "Doubting the TCR coreceptor function of CD8alphaalpha". Immunity. 28 (2): 149–159. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2008.01.005. PMID 18275828.
- 447Olivares-Villagómez D, Van Kaer L (November 2010). "TL and CD8αα: Enigmatic partners in mucosal immunity". Immunology Letters. 134 (1): 1–6.
- 448Mayassi T, Jabri B (September 2018). "Human intraepithelial lymphocytes". Mucosal Immunology. 11 (5): 1281–1289. doi:10.1038/s41385-018-0016-5. PMC 6178824. PMID 29674648.
- 449Sim GK (1995-01-01). "Intraepithelial lymphocytes and the immune system". Advances in Immunology. 58: 297–343. doi:10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60622-7. ISBN 9780120224586. PMID 7741030.
- 450McGhee JR (1998-01-01). "Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT)". In Delves PJ (ed.). Encyclopedia of Immunology (Second ed.). Elsevier. pp. 1774–1780. doi:10.1006/rwei.1999.0448. ISBN 9780122267659.
- 451Mayassi T, Jabri B (September 2018). "Human intraepithelial lymphocytes". Mucosal Immunology. 11 (5): 1281–1289. doi:10.1038/s41385-018-0016-5. PMC 6178824. PMID 29674648.
- 452Sim GK (1995-01-01). "Intraepithelial lymphocytes and the immune system". Advances in Immunology. 58: 297–343. doi:10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60622-7. ISBN 9780120224586. PMID 7741030.
- 453McGhee JR (1998-01-01). "Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT)". In Delves PJ (ed.). Encyclopedia of Immunology (Second ed.). Elsevier. pp. 1774–1780. doi:10.1006/rwei.1999.0448. ISBN 9780122267659.
- 454Cheroutre H (2015-01-01). "Chapter 35 - Intraepithelial TCRαβ T Cells in Health and Disease". In Mestecky J, Lefrancois L, Strober W, Russell MW, Kelsall BL (eds.). Mucosal Immunology (Fourth ed.). Academic Press. pp. 733–748. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-415847-4.00035-5. ISBN 9780124158474.
- 455
- 456
- 457
- 458Meresse B, Malamut G, Cerf-Bensussan N (June 2012). "Celiac disease: an immunological jigsaw". Immunity. 36 (6): 907–919. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2012.06.006. PMID 22749351.
- 459Li, Zhipeng; Wright, André-Denis G.; Yang, Yifeng; Si, Huazhe; Li, Guangyu (2017-01-18). "Unique Bacteria Community Composition and Co-occurrence in the Milk of Different Ruminants". Scientific Reports. 7: 40950. Bibcode:2017NatSR...740950L. doi:10.1038/srep40950. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 5241872. PMID 28098228.
- 460Venkataramana, Kandi; Padmavali, Palange; Ritu, Vaish; Adnan, Bashir Bhatti; Vinod, Kale; Maheshwar, Reddy Kandi; Mohan, Rao Bhoomagiri (August 2016). "Emerging Bacterial Infection: Identification and Clinical Significance of Kocuria Species". Cureus. 8 (8): e731. doi:10.7759/cureus.731. PMC 5017880. PMID 27630804.[/mfn} Kocuria kann normalerweise bei mesophilen Temperaturen überleben.460Reimer, Lorenz Christian; Carbasse, Joaquim Sardà; Koblitz, Julia; Ebeling, Christian; Podstawka, Adam; Overmann, Jörg (2022). "Kocuria rosea DSM 20447 is an aerobe, mesophilic bacterium of the family Micrococcaceae". BacDive. Retrieved 2022-11-07.
- 461Grice, Elizabeth; Kong, Heidi; Renaud, Gabriel; Young, Alice; Bouffard, Gerard; Blakesly, Robert; Wolfsberg, Tyra; Turner, Maria; Segre, Julia (July 2018). "A diversity profile of the human skin microbiota". Genome Research. 18 (7): 1043–1050. doi:10.1101/gr.075549.107. PMC 2493393. PMID 18502944.
- 462Ma, Edmond SK; Wong, Chris LP; Lai, Kristi TW; Chan, Edmond CH; Yam, WC; Chan, Angus CW (2005-07-19). "Kocuria kristinae infection associated with acute cholecystitis". BMC Infectious Diseases. 5 (1): 60. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-5-60. ISSN 1471-2334. PMC 1181815. PMID 16029488.
- 463Dotis, John; Printza, Nikoleta; Stabouli, Stella; Papachristou, Fotios (Jan–Feb 2015). "Kocuria Species Peritonitis: Although Rare, We Have To Care". Peritoneal Dialysis International. 35 (1): 26–30. doi:10.3747/pdi.2013.00138. PMC 4335924. PMID 24584591.
- 464Domont, Fanny; Le Flèche‐Matéos, Anne; Brémond‐Gignac, Dominique; Hamdad, Farida (2014-06-01). "Kocuria dacryocystitis infection, caused by Kocuria ocularis sp. nov". JMM Case Reports. 1 (2). doi:10.1099/jmmcr.0.002022. ISSN 2053-3721.
- 465Mattern, R.M.; Ding, Jiaxi (2014-02-27). "Keratitis with Kocuria palustris and Rothia mucilaginosa in Vitamin A Deficiency". Case Reports in Ophthalmology. 5 (1): 72–77. doi:10.1159/000360391. ISSN 1663-2699. PMC 3975196. PMID 24707276.
- 466Moreira, Jorge Salomão; Riccetto, Adriana Gut Lopes; da Silva, Marcos Tadeu Nolasco; Vilela, Maria Marluce dos Santos (January 2015). "Endocarditis by Kocuria rosea in an immunocompetent child". The Brazilian Journal of Infectious Diseases. 19 (1): 82–84. doi:10.1016/j.bjid.2014.09.007. ISSN 1413-8670. PMID 25523077.
- 467
- 468Lee, Mi Kyung; Choi, Soon Ho; Ryu, Dae Woong (2013-10-11). "Descending necrotizing Mediastinitis caused by Kocuria rosea: A case report". BMC Infectious Diseases. 13 (1): 475. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-13-475. ISSN 1471-2334. PMC 3852562. PMID 24112281.
- 469Tsai, Cheng-Yu; Su, Shou-hsin; Cheng, Yu-Hsin; Chou, Yu-lin; Tsai, Tai-Hsin; Lieu, Ann-Shung (2010-04-27). "Kocuria varians infection associated with brain abscess: A case report". BMC Infectious Diseases. 10 (1): 102. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-10-102. ISSN 1471-2334. PMC 2875226. PMID 20423506.
- 470Banerjee T, Singh A, Anurag, Pal S, Basu S. Emergence of Unusual Microorganisms in Microflora of Pilonidal Sinuses: A Multiple Case Series. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2023 Jan-Feb 01;50(1):26-30. doi: 10.1097/WON.0000000000000945. PMID: 36668986.
- 471Savini, V.; Catavitello, C.; Masciarelli, G.; Astolfi, D.; Balbinot, A.; Bianco, A.; Febbo, F.; D'Amario, C.; D'Antonio, D. (2010-09-30). "Drug sensitivity and clinical impact of members of the genus Kocuria". Journal of Medical Microbiology. 59 (12): 1395–1402. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.021709-0. ISSN 0022-2615. PMID 20884772.
- 472Vallalar, Bharathi (2012). "Investigation of the Growth and Survival of Bacteria from Mars Analog Environments When Exposed to Mars-like Conditions". Lsu Master's Theses.
- 473Marianne Abele-Horn: Antimikrobielle Therapie. Entscheidungshilfen zur Behandlung und Prophylaxe von Infektionskrankheiten. Unter Mitarbeit von Werner Heinz, Hartwig Klinker, Johann Schurz und August Stich, 2., überarbeitete und erweiterte Auflage. Peter Wiehl, Marburg 2009, ISBN 978-3-927219-14-4, S. 264.
- 474M. Haakensen, C. M. Dobson, J. E. Hill, B. Ziola: Reclassification of Pediococcus dextrinicus (Coster and White 1964) back 1978 (Approved Lists 1980) as Lactobacillus dextrinicus comb. nov., and emended description of the genus Lactobacillus. In: International journal of systematic and evolutionary microbiology. Band 59, Pt 3, März 2009, S. 615–621, ISSN 1466-5026. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.65779-0. PMID 19244449.
- 475Jinshui Zheng, Stijn Wittouck, Elisa Salvetti, Charles M.A.P. Franz, Hugh M.B. Harris: A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. In: International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. Band 70, Nr. 4, ISSN 1466-5034, S. 2782–2858, doi:10.1099/ijsem.0.004107 (microbiologyresearch.org
- 476Bernd Kerschner: Leaky Gut Syndrom: Mythos löchriger Darm. In: Medizin transparent. 5. Dezember 2017, abgerufen am 2. Oktober 2021.
- 477Seth C. Kalichman: Denying AIDS: Conspiracy Theories, Pseudoscience, and Human Tragedy. Springer Science & Business Media, 16. Januar 2009, ISBN 978-0-387-79476-1, S. 167.
- 478"Leaky gut syndrome". In: National Health Service. 18. Oktober 2017, archiviert vom Original; abgerufen am 28. Juli 2021 (englisch).
- 479Bernd Kerschner: Leaky Gut Syndrom: Mythos löchriger Darm. In: Medizin transparent. 5. Dezember 2017, abgerufen am 2. Oktober 2021.
- 480"Leaky gut syndrome". In: National Health Service. 18. Oktober 2017, archiviert vom Original; abgerufen am 28. Juli 2021 (englisch).
- 481Debunking the Myth of ‘Leaky Gut Syndrome’. (en) In: badgut.org. Gastrointestinal Society, abgerufen am 4. Dezember 2020.
- 482Günther Heepen: Hilfe aus der Natur bei Leaky-Gut-Syndrom, Darmpilzen, Reizmagen, Allergien und Verstopfung. Gräfe und Unzer Verlag, 7. August 2017, ISBN 978-3-833-86294-6, S. 107.
- 483T. Vanuytsel, S. Vermeire, I. Cleynen: The role of Haptoglobin and its related protein, Zonulin, in inflammatory bowel disease. In: Tissue barriers. Band 1, Nummer 5, Dezember 2013, S. e27321, doi:10.4161/tisb.27321, PMID 24868498, PMC 3943850 (freier Volltext) (Review).
- 484Charles Janeway et al. Immunobiology. 5. Auflage. Garland Science, New York 2001, ISBN 3-8274-1079-7 (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov).
- 485R. P. McEver: Selectins: initiators of leucocyte adhesion and signalling at the vascular wall. In: Cardiovascular research. Band 107, Nummer 3, August 2015, S. 331–339, doi:10.1093/cvr/cvv154, PMID 25994174, PMC 4592324 (freier Volltext) (Review).
- 486
- 487Coakley et al.: Assessing chemokine co-receptor usage in HIV. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2005 Feb;18(1):9-15.
- 488Weiße Blutkörperchen – gefangen in der Blutbahn! Seltene Erbkrankheit bei Kindern erforscht. 28. Mai 2001, innovations-report.de, abgerufen am 30. Mai 2009.
- 489Warum Nutztierrassen verschwinden. In: Die Tageszeitung. 21. April 2008 (taz.de).
- 490Meyers Konversations-Lexikon, 4. Auflage von 1888–1890.
- 491Eintrag zu Linolsäure. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, abgerufen am 22. Juni 2013.
- 492Eintrag zu Safloröl. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, abgerufen am 22. Juni 2013.
- 493Eintrag zu Hanföl. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, abgerufen am 22. Juni 2013.
- 494Eintrag zu Linolsäure. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, abgerufen am 22. Juni 2013.
- 495H. J. Bestmann, M. Pietschmann, K. Steinmeier, O. Vostrowsky: Flüchtige Inhaltsstoffe von Crotalaria ochroleuca und deren Wirkung auf Schadinsekten / Volatile Constituents from Crotalaria ochroleuca and Their Effect on Pest Insects. In: Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C. 46, 1991, S. 579–584 (PDF, freier Volltext).
- 496Jürgen Blecker: Chemie für jedermann. Compact Verlag, 2010, ISBN 3-8174-7856-9, S. 373 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- 497RKI: Epidemiologisches Bulletin Nr. 3/2020, vom 16. Januar 2020, S. 18, für 2019: 591 Fälle, im Vergleich dazu 13636 Salmonellose-Fälle
- 498Lachs von Coop, Migros und Volg wegen Listerien zurückgerufen. In: derbund.ch. 9. März 2019, abgerufen am 11. März 2019.
- 499Listerien in Frikadellen: Betriebszulassung ruht. In: ndr.de. 3. November 2019, abgerufen am 3. November 2019.
- 500Wilhelm Gemoll: Griechisch-Deutsches Schul- und Handwörterbuch. München/ Wien 1965.
- 501Abul K. Abbas, Andrew Lichtman, Shiv Pillai: Cellular and Molecular Immunology. 6. Auflage. Saunders Elsevier, 2007, S. 30.
- 502Edward D. Harris, Biochemical Facts behind the Definition and Properties of Metabolites (englisch). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Abgerufen am 2. Mai 2016.
- 503Wilhelm Pape, Max Sengebusch (Bearb.): Handwörterbuch der griechischen Sprache. 3. Auflage, 6. Abdruck. Vieweg & Sohn, Braunschweig 1914 (zeno.org [abgerufen am 12. September 2019]).
- 504Friedrich Kluge, Alfred Götze: Etymologisches Wörterbuch der deutschen Sprache. 20. Auflage. Hrsg. von Walther Mitzka. De Gruyter, Berlin / New York 1967; Neudruck („21. unveränderte Auflage“) ebenda 1975, ISBN 3-11-005709-3, S. 478.
- 505Deutsche Gesellschaft für Neurologie, federführend HC Diener: S1-Leitlinie Therapie der Migräne, Abschnitt Epidemiologie. In: Leitlinien für Diagnostik und Therapie in der Neurologie. Kapitel Kopfschmerzen und andere Schmerzen. Stand September 2012 in der Fassung vom 21. März 2013, AWMF-Registriernummer 030 - 057
- 506Filip K. Swirski u. a.: Identification of Splenic Reservoir Monocytes and Their Deployment to Inflammatory Sites. In: Science. 325, 2009, S. 612–616.
- 507J. Heitman, N. R. Movva, M. N. Hall: Targets for cell cycle arrest by the immunosuppressant rapamycin in yeast. In: Science. Nr. 253, 1991, S. 905–909, PMID 1715094.
- 508Ushma S. Neill: A conversation with Michael Hall. In: Journal of Clinical Investigation. Band 127, Nr. 11, 1. November 2017, ISSN 0021-9738, S. 3916–3917, doi:10.1172/JCI97760 (jci.org [abgerufen am 23. Mai 2023]).
- 509N. Hay, N. Sonenberg: Upstream and downstream of mTOR. In: Genes Dev. Nr. 18, 2004, S. 1926–1945 (Artikel). PMID 15314020
- 510Xuemin Wang, Christopher G. Proud: The mTOR Pathway in the Control of Protein Synthesis. In: Physiology. Nr. 21, 2006, S. 362–369 (Artikel).
- 511Janet E. Dancey: MTOR and Related Pathways. In: Cancer Biology & Therapy. Nr. 5, 2006, S. 1065–1073 (PDF).
- 512Janet E. Dancey: MTOR and Related Pathways. In: Cancer Biology & Therapy. Nr. 5, 2006, S. 1065–1073 (PDF).
- 513G. Blaeser-Kiel: Sirolimus zum Transplantatschutz. Bessere Langzeitprognose durch geringere Tumorinzidenz. In: Deutsches Ärzteblatt. Nr. 104, 2007, S. A-1255 (Artikel).
- 514Henrik Ekberg et al.: Reduced Exposure to Calcineurin Inhibitors in Renal Transplantation. In: N Engl J Med. Nr. 357, 2007, S. 2561–2575 (Abstract).
- 515Gary Hudes et al.: Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. In: N Engl J Med. Nr. 356, 2007, S. 2271–2281, PMID 17538086.
- 516W. Kühn, G. Walz: Autosomal dominante polyzystische Nierenerkrankung. In: Dtsch Arztebl. Band 104, Nr. 44, 2007, S. 3022–3028 (Artikel).
- 517Wilfred Lieberthal, Jerrold S Levine: The role of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in renal disease. In: Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. Band 20, Nr. 12, Dezember 2009, S. 2493–2502, doi:10.1681/ASN.2008111186, PMID 19875810.
- 518John J. Bissler et al.: Sirolimus for Angiomyolipoma in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex or Lymphangioleiomyomatosis. In: N Engl J Med. Nr. 358, 2008, S. 140–151 (Abstract).
- 519Matthias Krams u. a.: Kurzlehrbuch Pathologie. 2. Auflage. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 2013, ISBN 978-3-13-143252-0, S. 17–31.
- 520Ursus-Nikolaus Riede, Martin Werner (Hrsg.): Allgemeine und Spezielle Pathologie. 2. Auflage. Springer Verlag, Berlin/ Heidelberg, 2017, ISBN 978-3-662-48725-9, S. 55f.
- 521Matthias Krams u. a.: Kurzlehrbuch Pathologie. 2. Auflage. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 2013, ISBN 978-3-13-143252-0, S. 31.
- 522Aussprache: En-ef-kappa-be. Die Bezeichnung ist darauf zurückzuführen, dass NF-κB zuerst beschrieben wurde als ein im Zellkern (Nucleus) reifer B-Lymphozyten vorhandenes Protein, das an ein DNA-Motiv im Transkriptionsverstärker des Gens für die κ-Kette der Immunglobuline bindet (Sen und Baltimore 1986). Nach und nach wurde jedoch gezeigt, dass NF-κB in allen Zellen des Organismus vorhanden ist; der Name wurde jedoch beibehalten.
- 523
- 524Eintrag zu Nicotinamid-Adenin-Dinucleotid. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, abgerufen am 9. Dezember 2014.
- 525A. Harden, W. J. Young: The alcoholic ferment of Yeast-juice. In: Proceedings of the Royal Society of London (Series B, Containing Papers of a Biological Character ed.), Band 78, Nr. 526, Oktober 1906, S. 369–375. (doi:10.1098/rspb.1906.0029).
- 526Eintrag zu Nicotinamid-Adenin-Dinucleotid. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, abgerufen am 9. Dezember 2014.
- 527Pschyrembel, Medizinisches Wörterbuch, 257. Auflage, 1993
- 528ICTV: ICTV Taxonomy history: Alphapapillomavirus 1, EC 51, Berlin, Germany, July 2019; Email ratification March 2020 (MSL #35)
- 529Annabel Rector, Marc Van Ranst: Animal papillomaviruses, Virology Band 445, Ausgabe 1–2, Oktober 2013, S. 213–223, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2013.05.007
- 530Ryan KJ; Ray CG, eds. (2004). Sherris Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). McGraw Hill. ISBN 0-8385-8529-9.
- 531Higaki S, Kitagawa T, Kagoura M, Morohashi M, Yamagishi T (2000). "Characterization of Peptostreptococcus species in skin infections". J Int Med Res. 28 (3): 143–7. doi:10.1177/147323000002800305. PMID 10983864. S2CID 30682359.
- 532Hoffman, Barbara (2012). Williams gynecology (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. 65. ISBN 978-0071716727.
- 533Senok, Abiola C; Verstraelen, Hans; Temmerman, Marleen; Botta, Giuseppe A; Senok, Abiola C (2009). "Probiotics for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (4): CD006289. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006289.pub2. PMID 19821358.
- 534Mader JT, Calhoun J (1996). Baron S, et al. (eds.). Bone, Joint, and Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections. In: Baron's Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). Univ of Texas Medical Branch. ISBN 0-9631172-1-1.
- 535Brook I. Treatment of anaerobic infection. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2007; 5:991-1006
- 536Finegold SM. Anaerobic Bacteria in Human Disease. Orlando, Fla: Academic Press; 1977.
- 537Brook I. Anaerobic Infections. In: Diagnosis and Management. 4th Edition. New York: Informa Healthcare USA Inc.; 2007.
- 538Brook I. Recovery of anaerobic bacteria from clinical specimens in 12 years at two military hospitals. J Clin Microbiol. Jun 1988;26(6)1181-8.
- 539Brook I. Anaerobic Infections. In: Diagnosis and Management. 4th Edition. New York: Informa Healthcare USA Inc.; 2007.
- 540Bourgault AM, Rosenblatt JE, Fitzgerald RH. Peptococcus magnus: a significant human pathogen. Ann Intern Med. Aug 1980;93(2):244-8.
- 541Brook I. Peptostreptococcal infection in children. Scand J Infect Dis. 1994;26(5)503-10.
- 542Araki H, Kuriyama T, Nakagawa K, Karasawa T. The microbial synergy of Peptostreptococcus micros and Prevotella intermedia in a urine abscess model. Oral Microbiol Immunol. Jun 2004;19(3):177-81.
- 543Brook I. Anaerobic Infections. In: Diagnosis and Management. 4th Edition. New York: Informa Healthcare USA Inc.; 2007.
- 544Martin WJ. Isolation and identification of anaerobic bacteria in the clinical laboratory. A 2-year experience. Mayo Clin Proc. May 1974;49(5):300-8.
- 545Martin WJ. Isolation and identification of anaerobic bacteria in the clinical laboratory. A 2-year experience. Mayo Clin Proc. May 1974;49(5):300-8.
- 546Mya Breitbart, Forest Rohwer: Here a virus, there a virus, everywhere the same virus?. In: Trends in Microbiology. 13, Nr. 6, April, S. 278–284. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2005.04.003.
- 547Mark L. Wickstrom, Charles T. Robbins, Thomas A. Hanley, Donald E. Spalinger, Steven M. Parish: Food Intake and Foraging Energetics of Elk and Mule Deer. In: The Journal of Wildlife Management. 48, Nr. 4, 1984, S. 1285–1301. doi:10.2307/3801789.
- 548Gary E. Belovsky: Optimal foraging and community structure: The allometry of herbivore food selection and competition. In: Evolutionary Ecology. 11, Nr. 6, 1997, S. 641–672. doi:10.1023/A:1018430201230.
- 549R.H.V Bell: The use of the herb layer by grazing ungulates in the Serengeti National Park, Tanzania. University of Manchester, 1969.
- 550P.J. Jarman: The Social Organisation of Antelope in Relation to Their Ecology. In: Behaviour. 48, Nr. 3/4, 1974, S. 215–267.
- 551Anthony R.E. Sinclair, Simon Mduma, Justin S. Brashares: Patterns of predation in a diverse predator–prey system. In: Nature. Nr. 425, 2003, S. 288–290. doi:10.1038/nature01934.
- 552R. Norman Owen-Smith: Megaherbivores: The influence of very large body size on ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- 553R. Norman Owen-Smith: Niche separation among African ungulates. In: Species and speciation. 4, 1985, S. 167–171.
- 554John Damuth, Christine M. Janis: On the relationship between hypsodonty and feeding ecology in ungulate mammals, and its utility in palaeoecology. In: Biological Reviews. 86, April, S. 733–758. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.2011.00176.x.
- 555John Damuth, Christine M. Janis: On the relationship between hypsodonty and feeding ecology in ungulate mammals, and its utility in palaeoecology. In: Biological Reviews. 86, April, S. 733–758. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.2011.00176.x.
- 556R. Norman Owen-Smith: Megaherbivores: The influence of very large body size on ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- 557Neil A. Campbell: Biologie. Hrsg.: Jürgen Markl. 1., korrigierter Nachdruck Auflage. Spektrum, Heidelberg/ Berlin/ Oxford 1998, ISBN 3-8274-0032-5, S. 80 (englisch: Biology. 1996.).
- 558Mulder: Ueber die Zusammensetzung einiger thierischer Substanzen. In: Journal für praktische Chemie. Band 16, 1839, S. 129–152 (Digitalisat).
- 559Duden – Deutsches Universalwörterbuch. 4. Auflage. Mannheim 2001.
- 560Theodor Wieland: History of Peptide Chemistry, in: Bernd Gutte (Hrsg.), Peptides, Academic Press 1995, S. 2
- 561International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium: Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome. In: Nature. Band 431, Nr. 7011, 2004, S. 931–945, doi:10.1038/nature03001, PMID 15496913.
- 562International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium: Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. In: Nature. Band 409, Nr. 6822, 2001, S. 860–921, doi:10.1038/35057062, PMID 11237011.
- 563P. Kapranov u. a.: Examples of the complex architecture of the human transcriptome revealed by RACE and high-density tiling arrays. In: Genome Research. Band 15, Nr. 7, 2005, S. 987–997, PMID 15998911.
- 564J. L. Rupert: Genomics and environmental hypoxia: what (and how) we can learn from the transcriptome. In: High Alt Med Biol. Band 9, Nr. 2, 2008, S. 115–122, PMID 18578642.
- 565E. Pennisi: Genomics. DNA study forces rethink of what it means to be a gene. In: Science. Band 15, Nr. 316, 2007, S. 1556–1557, PMID 17569836.
- 566E. R. Stadtman, R. L. Levine: Chemical modification of proteins by reactive oxygen species. In: I. Dalle-Donne, A. Scaloni, A. Butterfield (Hrsg.): Redox Proteomics: From Protein Modifications To Cellular Dysfunction And Diseases. (= Wiley-Interscience Series on Mass Spectrometry). 2006, ISBN 0-471-72345-2.
- 567DGE: Referenzwerte Protein, abgerufen am 7. Oktober 2017.
- 568Dietary protein quality evaluation in human nutrition. Report of an FAQ Expert Consultation. In: FAO (Hrsg.): FAO food and nutrition paper. Band 92, Rom 2013, S. 1–66, PMID 26369006, ISBN 978-92-5-107417-6.
- 569R. Elango, M. A. Humayun, R. O. Ball, P. B. Pencharz: Evidence that protein requirements have been significantly underestimated. In: Current opinion in clinical nutrition and metabolic care. Band 13, Nummer 1, Januar 2010, S. 52–57, doi:10.1097/MCO.0b013e328332f9b7, PMID 19841581 (Review).
- 570DGE: Reference Values for Nutrient Intake (Memento vom 15. September 2009 im Internet Archive), Umschau/ Braus, Frankfurt am Main 2000, ISBN 3-8295-7114-3, S. 31.
- 571Can eating too much protein be bad for you? 26. August 2019, abgerufen am 29. Januar 2020 (englisch).
- 572zit. nach Cornelia Pfaff: Sporternährung: Was ist dran an Eiweißpulver, L-Carnitin und Co? 19. Oktober 2002, abgerufen am 9. Dezember 2019.
- 573Vegane Protein-Quellen in Lebensmitteln. 5. Oktober 2017, abgerufen am 19. Januar 2018.
- 574Sun Yangbo, Liu Buyun, Snetselaar Linda G., Wallace Robert B., Shadyab Aladdin H.: Association of Major Dietary Protein Sources With All‐Cause and Cause‐Specific Mortality: Prospective Cohort Study. In: Journal of the American Heart Association. Band 0, Nr. 0, S. e015553, doi:10.1161/JAHA.119.015553 (ahajournals.org [abgerufen am 28. Februar 2021]).
- 575Harvard T.H. Chang School of Public Health: Protein. 18. September 2012, abgerufen am 28. Februar 2021 (amerikanisches Englisch).
- 576Mingyang Song, Teresa T. Fung, Frank B. Hu, Walter C. Willett, Valter D. Longo: Association of Animal and Plant Protein Intake With All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality. In: JAMA Internal Medicine. Band 176, Nr. 10, 1. Oktober 2016, ISSN 2168-6106, S. 1453, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.4182 (jamanetwork.com [abgerufen am 28. Februar 2021]).
- 577Mingyang Song, Teresa T. Fung, Frank B. Hu, Walter C. Willett, Valter D. Longo: Association of Animal and Plant Protein Intake With All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality. In: JAMA Internal Medicine. Band 176, Nr. 10, 1. Oktober 2016, ISSN 2168-6106, S. 1453, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2016.4182 (jamanetwork.com [abgerufen am 28. Februar 2021]).
- 578Protein and amino acid requirements in human nutrition. Report of a joint FAO/WHO/UNU expert consultation (WHO Technical Report Series 935). Weltgesundheitsorganisation, 2007, ISBN 92-4120935-6 (Volltext [PDF]).
- 579Gertjan Schaafsma: The Protein Digestibility–Corrected Amino Acid Score. In: The Journal of Nutrition. Band 130, Nr. 7, 2000, S. 1865S–1867S, doi:10.1093/jn/130.7.1865S (freier Volltext).
- 580C. P. Marinangeli, J. D. House: Potential impact of the digestible indispensable amino acid score as a measure of protein quality on dietary regulations and health. In: Nutrition reviews. Band 75, Nummer 8, August 2017, S. 658–667, doi:10.1093/nutrit/nux025, PMID 28969364, PMC 5914309 (freier Volltext) (Review).
- 581R. R. Wolfe, S. M. Rutherfurd, I. Y. Kim, P. J. Moughan: Protein quality as determined by the Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score: evaluation of factors underlying the calculation. In: Nutrition reviews. Band 74, Nr 9, 2016, S. 584–599, doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuw022, PMID 27452871 (Review).
- 582S. M. Phillips: The impact of protein quality on the promotion of resistance exercise-induced changes in muscle mass. In: Nutrition & metabolism. Band 13, 2016, S. 64, doi:10.1186/s12986-016-0124-8, PMID 27708684, PMC 5041535 (freier Volltext) (Review).
- 583Bedeutung, Definition und Berechnung des DIAAS´ Wissenschaftlicher Bericht zur Biologischen Wertigkeit in deutscher Sprache - DIAAS. Abgerufen am 24. August 2020.
- 584Fachagentur Nachwachsende Rohstoffe e. V. (Hrsg.): Daten und Fakten zu nachwachsenden Rohstoffen. Gülzow 2006, S. 57. (PDF-Download).
- 585Ralf Pude, Barbara Wenig: Pflanzen für die Industrie. Pflanzen, Rohstoffe, Produkte. Fachagentur Nachwachsende Rohstoffe e. V., Gülzow 2005, S. 11. (PDF-Download).
- 586Dominik Vogt, Christian Gahle, Michael Karus: Erstellung eines Überblicks zu Marktsituation und Trends zur stofflichen Nutzung nachwachsender Rohstoffe (NR) in Nordrhein-Westfalen. nova-Institut GmbH, Hürth 2005.
- 587K. Rappold: Gelatine – Ein natürliches Nahrungsmittel. In: bmi aktuell. 1/2004, Hrsg. Informationszentrale für Backmittel und Backgrundstoffe zur Herstellung von Brot und Feinen Backwaren e. V.
- 588Homepage Gelatine Manufacturers of Europe (Memento des Originals vom 9. Januar 2016 im Internet Archive) i Info: Der Archivlink wurde automatisch eingesetzt und noch nicht geprüft. Bitte prüfe Original- und Archivlink gemäß Anleitung und entferne dann diesen Hinweis., Abgerufen 18. September 2008.
- 589Homepage Gelatine Manufacturers of Europe (Memento des Originals vom 9. Januar 2016 im Internet Archive) i Info: Der Archivlink wurde automatisch eingesetzt und noch nicht geprüft. Bitte prüfe Original- und Archivlink gemäß Anleitung und entferne dann diesen Hinweis., Abgerufen 18. September 2008.
- 590Johann Verbeek, Lisa van den Berg: Proteinous Bioplastics from Bloodmeal. In: bioplastics magazine. Nr. 5, 2008, S. 30.
- 591Casparus J. R. Verbeek, Lisa E. van den Berg: Development of Proteinous Bioplastics Using Bloodmeal. In: Journal of Polymers and the Environment. Band 19, Nr. 1, 2010, S. 1–10, doi:10.1007/s10924-010-0232-x (freier Volltext).
- 592Matthias Geuder: Biopolymere – Rohstoffe, Technologien, Anwendungen. In: Biowerkstoff-Report. Okt./Nov./Dez. 2008, S. 46. (PDF; 5,2 MB).
- 593Flottweg Industriezentrifugen für pflanzliche und tierische Proteine. Abgerufen am 22. Mai 2017.
- 594
- 595Claus Stäcker: Die Herren der Fliegen (Memento vom 24. Februar 2013 im Internet Archive). In: tagesschau.de.
- 596AgriProtein's managing director sees maggots as next protein alternative. In: efeedlink.com. Abgerufen am 3. Februar 2016.
- 597AgriProtein's managing director sees maggots as next protein alternative. In: efeedlink.com. Abgerufen am 3. Februar 2016.
- 598Claus Stäcker: Die Herren der Fliegen (Memento vom 24. Februar 2013 im Internet Archive). In: tagesschau.de.
- 599Rob Fletcher: Fishmeal replacement scoops major award. In: fishnewseu.com. Fish News EU, abgerufen am 3. Februar 2016.
- 600Maggots are Turf over Surf animal feed alternative. In: Reuters. 16. März 2012 (reuters.com).
- 601
- 602Claudia Bröll: Nachhaltige Geschäftsidee Made in South Africa. In: Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung. 15. August 2012 (faz.net).
- 603Jessica Hendy: Ancient protein analysis in archaeology. In: Science Advances. Band 7, Nr. 3, 2021, eabb9314, doi:10.1126/sciadv.abb9314.
- 604Michelle Starr: Scientists Claim to Have Found The First Known Extraterrestrial Protein in a Meteorite. In: ScienceAlert.com, 2. März 2020.
- 605Protein discovered inside a meteorite, Phys.org. 3. März 2020. Abgerufen am 4. März 2020.
- 606https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.11688
- 607taxonomy. "Taxonomy browser (Ruminococcus)". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2016-04-05.
- 608Iannotti EL, Kafkewitz D, Wolin MJ, Bryant MP (June 1973). "Glucose fermentation products in Ruminococcus albus grown in continuous culture with Vibrio succinogenes: changes caused by interspecies transfer of H 2". Journal of Bacteriology. 114 (3): 1231–40. doi:10.1128/JB.114.3.1231-1240.1973. PMC 285387. PMID 4351387.
- 609Iannotti EL, Kafkewitz D, Wolin MJ, Bryant MP (June 1973). "Glucose fermentation products in Ruminococcus albus grown in continuous culture with Vibrio succinogenes: changes caused by interspecies transfer of H 2". Journal of Bacteriology. 114 (3): 1231–40. doi:10.1128/JB.114.3.1231-1240.1973. PMC 285387. PMID 4351387.
- 610Ze, Xiaolei; Duncan, Sylvia H.; Louis, Petra; Flint, Harry J. (2012). "Ruminococcus bromii is a keystone species for the degradation of resistant starch in the human colon". The ISME Journal. 6 (8): 1535–1543. doi:10.1038/ismej.2012.4. PMC 3400402. PMID 22343308.
- 611Nagao-Kitamoto H, Kamada N (February 2017). "Host-microbial Cross-talk in Inflammatory Bowel Disease". Immune Network. 17 (1): 1–12. doi:10.4110/in.2017.17.1.1. PMC 5334117. PMID 28261015.
- 612Nagao-Kitamoto H, Kamada N (February 2017). "Host-microbial Cross-talk in Inflammatory Bowel Disease". Immune Network. 17 (1): 1–12. doi:10.4110/in.2017.17.1.1. PMC 5334117. PMID 28261015.
- 613Henke, Matthew T.; Kenny, Douglas J.; Cassilly, Chelsi D.; Vlamakis, Hera; Xavier, Ramnik J.; Clardy, Jon (2019-06-25). "Ruminococcus gnavus, a member of the human gut microbiome associated with Crohn's disease, produces an inflammatory polysaccharide". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 116 (26): 12672–12677. doi:10.1073/pnas.1904099116. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 6601261. PMID 31182571.
- 614Im Test: Sauerkraut (PDF; 32 KiB) (Memento vom 30. August 2017 im Internet Archive); Vitamin K in Lebensmitteln (PDF; 80 KiB) (Memento vom 14. August 2018 im Internet Archive); S.W. Souci/ W. Fachmann/ H. Kraut: Die Zusammensetzung der Lebensmittel – Nährwert-Tabellen. 7. Auflage. 2008, ISBN 978-3-8047-5038-8.
- 615HautinForm. Das Magazin aus der Hautarztpraxis. Berufsverband der Deutschen Dermatologen e. V. (uptoderm.de (Memento des Originals vom 16. Dezember 2013 im Internet Archive) 3-2013, S. 8.
- 616Psoriasis (Übersicht) – Fachbereich Dermatologie – Altmeyers Enzyklopädie. Abgerufen am 28. Oktober 2017.
- 617Childs BG, Durik M, Baker DJ, van Deursen JM (December 2015). "Cellular senescence in aging and age-related disease: from mechanisms to therapy". Nature Medicine. 21 (12): 1424–1435. doi:10.1038/nm.4000. PMC 4748967. PMID 26646499.
- 618Kirkland JL, Tchkonia T (August 2015). "Clinical strategies and animal models for developing senolytic agents". Experimental Gerontology. 68: 19–25. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2014.10.012. PMC 4412760. PMID 25446976.
- 619van Deursen JM (May 2019). "Senolytic therapies for healthy longevity". Science. 364 (6441): 636–637. Bibcode:2019Sci...364..636V. doi:10.1126/science.aaw1299. PMC 6816502. PMID 31097655.
- 620Chambers ES, Akbar AN (2020). "Can blocking inflammation enhance immunity during aging?". The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 145 (5): 1323–1331. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.03.016. PMID 32386656.
- 621Hu, Qinchao; Peng, Jianmin; Jiang, Laibo; Li, Wuguo; Su, Qiao; Zhang, Jiayu; Li, Huan; Song, Ming; Cheng, Bin; Xia, Juan; Wu, Tong (28 October 2020). "Metformin as a senostatic drug enhances the anticancer efficacy of CDK4/6 inhibitor in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma". Cell Death & Disease. 11 (10): 925. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-03126-0. PMC 7595194. PMID 33116117.
- 622Kirkland JL, Tchkonia T (November 2020). "Senolytic drugs: from discovery to translation". Journal of Internal Medicine. 288 (5): 518–536. doi:10.1111/joim.13141. PMC 7405395. PMID 32686219.
- 623
- 624Blagosklonny MV (December 2013). "Selective anti-cancer agents as anti-aging drugs". Cancer Biology & Therapy. 14 (12): 1092–1097. doi:10.4161/cbt.27350. PMC 3912031. PMID 24345884.
- 625Blagosklonny MV (December 2013). "Selective anti-cancer agents as anti-aging drugs". Cancer Biology & Therapy. 14 (12): 1092–1097. doi:10.4161/cbt.27350. PMC 3912031. PMID 24345884.
- 626Sean J. Morrison, Nirao M. Shah, David J. Anderson: Review: Regulatory mechanisms in stem cell biology. In: Cell. Band 88, Nr. 3, 1997, S. 287–298, doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81867-X. PMID 9039255. (Volltext; PDF; 260 kB) (PDF)
- 627Eugene V. Koonin: The origin and early evolution of eukaryotes in the light of phylogenomics. In: Genome Biology. 2010. 11:209. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-209
- 628Ralf Vollmuth: Staphylokokken, Staphylococcus. In: Werner E. Gerabek, Bernhard D. Haage, Gundolf Keil, Wolfgang Wegner (Hrsg.): Enzyklopädie Medizingeschichte. De Gruyter, Berlin/ New York 2005, ISBN 3-11-015714-4, S. 1355.
- 629Wilhelm Gemoll: Griechisch-Deutsches Schul- und Handwörterbuch. Freytag, München/ Wien 1965.
- 630Eintrag zu Synbiotika. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, abgerufen am 27. Juni 2012.
- 631Synbiotika im Vitalingo-Lexikon, abgerufen am 27. Juni 2012.
- 632Carcinogenesis 19, 281–285 (1997).
- 633Rock FL, Hardiman G, Timans JC, Kastelein RA, Bazan JF (January 1998). "A family of human receptors structurally related to Drosophila Toll". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 95 (2): 588–93. Bibcode:1998PNAS...95..588R. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.2.588. PMC 18464. PMID 9435236.
- 634
- 635
- 636Kim SJ, Chen Z, Chamberlain ND, Essani AB, Volin MV, Amin MA, Volkov S, Gravallese EM, Arami S, Swedler W, Lane NE, Mehta A, Sweiss N, Shahrara S (October 2014). "Ligation of TLR5 promotes myeloid cell infiltration and differentiation into mature osteoclasts in rheumatoid arthritis and experimental arthritis". Journal of Immunology. Baltimore, Md. 193 (8): 3902–13. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1302998. PMC 4185216. PMID 25200955.
- 637Badr MT, Häcker G (2019). "Gene expression profiling meta-analysis reveals novel gene signatures and pathways shared between tuberculosis and rheumatoid arthritis". PLOS ONE. 14 (3): e0213470. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0213470. PMC 6405138. PMID 30845171.
- 638Kassem A, Henning P, Kindlund B, Lindholm C, Lerner UH (November 2015). "TLR5, a novel mediator of innate immunity-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone loss". FASEB Journal. 29 (11): 4449–60. doi:10.1096/fj.15-272559. PMID 26207027.
- 639Castaño-Rodríguez N, Kaakoush NO, Mitchell HM (2014-01-01). "Pattern-recognition receptors and gastric cancer". Frontiers in Immunology. 5: 336. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00336. PMC 4105827. PMID 25101079.
- 640Husseinzadeh N, Davenport SM (November 2014). "Role of toll-like receptors in cervical, endometrial and ovarian cancers: a review". Gynecologic Oncology. 135 (2): 359–63. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2014.08.013. PMID 25135000.
- 641Sharma N, Akhade AS, Qadri A (April 2013). "Sphingosine-1-phosphate suppresses TLR-induced CXCL8 secretion from human T cells". Journal of Leukocyte Biology. 93 (4): 521–8. doi:10.1189/jlb.0712328. PMID 23345392.
- 642
- 643Hayashi F, Smith KD, Ozinsky A, Hawn TR, Yi EC, Goodlett DR, et al. (April 2001). "The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5". Nature. 410 (6832): 1099–103. Bibcode:2001Natur.410.1099H. doi:10.1038/35074106. PMID 11323673. S2CID 4422702.
- 644Smith KD, Andersen-Nissen E, Hayashi F, Strobe K, Bergman MA, Barrett SL, et al. (December 2003). "Toll-like receptor 5 recognizes a conserved site on flagellin required for protofilament formation and bacterial motility". Nature Immunology. 4 (12): 1247–53. doi:10.1038/ni1011. PMID 14625549. S2CID 6157006.
- 645Andersen-Nissen E, Smith KD, Strobe KL, Barrett SL, Cookson BT, Logan SM, Aderem A (June 2005). "Evasion of Toll-like receptor 5 by flagellated bacteria". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 102 (26): 9247–52. Bibcode:2005PNAS..102.9247A. doi:10.1073/pnas.0502040102. PMC 1166605. PMID 15956202.
- 646
- 647Gewirtz AT, Navas TA, Lyons S, Godowski PJ, Madara JL (August 2001). "Cutting edge: bacterial flagellin activates basolaterally expressed TLR5 to induce epithelial proinflammatory gene expression". Journal of Immunology. 167 (4): 1882–5. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.167.4.1882. PMID 11489966. S2CID 23844864.
- 648Choi YJ, Jung J, Chung HK, Im E, Rhee SH (January 2013). "PTEN regulates TLR5-induced intestinal inflammation by controlling Mal/TIRAP recruitment". FASEB Journal. 27 (1): 243–54. doi:10.1096/fj.12-217596. PMC 3528317. PMID 23038756.
- 649Rhee SH, Kim H, Moyer MP, Pothoulakis C (July 2006). "Role of MyD88 in phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation by flagellin/toll-like receptor 5 engagement in colonic epithelial cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (27): 18560–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M513861200. PMID 16644730.
- 650

IRAK-4 gehört zur IRAK-Familie und ist eine Proteinkinase, die an der Signalisierung angeborener Immunreaktionen durch Toll-like-Rezeptoren beteiligt ist. Sie unterstützt auch die Signalübertragung durch T-Zell-Rezeptoren. IRAK4 enthält Domänenstrukturen, die denen von IRAK1, IRAK2, IRAKM und Pelle ähnlich sind. IRAK4 ist im Vergleich zu IRAK1, IRAK2 und IRAKM insofern einzigartig, als es stromaufwärts von den anderen IRAKs funktioniert, aber in dieser Eigenschaft Pelle ähnlicher ist. IRAK4 hat wichtige klinische Anwendungen. Tiere ohne IRAK4 sind anfälliger für Viren und Bakterien, aber völlig resistent gegen LPS. - 651

Die Interleukin-1-Rezeptor-assoziierte Kinase 1 (IRAK-1) ist ein Enzym, das beim Menschen durch das IRAK1-Gen kodiert wird. IRAK-1 spielt eine wichtige Rolle bei der Regulierung der Expression von Entzündungsgenen durch Immunzellen wie Monozyten und Makrophagen, die wiederum das Immunsystem bei der Beseitigung von Bakterien, Viren und anderen Krankheitserregern unterstützen. IRAK-1 gehört zur IRAK-Familie, die aus IRAK-1, IRAK-2, IRAK-3 und IRAK-4 besteht, und wird durch Entzündungsmoleküle aktiviert, die während eines pathogenen Angriffs durch Signalwege freigesetzt werden. IRAK-1 wird als ein Kinase-Enzym eingestuft, das Wege sowohl im angeborenen als auch im adaptiven Immunsystem reguliert. - 652Gohda J, Matsumura T, Inoue J (September 2004). "Cutting edge: TNFR-associated factor (TRAF) 6 is essential for MyD88-dependent pathway but not toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor-inducing IFN-beta (TRIF)-dependent pathway in TLR signaling". Journal of Immunology. 173 (5): 2913–7. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.173.5.2913. PMID 15322147.
- 653Moors MA, Li L, Mizel SB (July 2001). "Activation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase by gram-negative flagellin". Infection and Immunity. 69 (7): 4424–9. doi:10.1128/IAI.69.7.4424-4429.2001. PMC 98515. PMID 11401982.
- 654

Der Nuklearfaktor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) ist ein Proteinkomplex, der die Transkription der DNA, die Zytokinproduktion und das Überleben der Zellen steuert. NF-κB kommt in fast allen tierischen Zelltypen vor und ist an den zellulären Reaktionen auf Stimuli wie Stress, Zytokine, freie Radikale, Schwermetalle, ultraviolette Strahlung, oxidiertes LDL und bakterielle oder virale Antigene beteiligt. NF-κB spielt eine Schlüsselrolle bei der Regulierung der Immunantwort auf Infektionen. Eine fehlerhafte Regulierung von NF-κB wurde mit Krebs, Entzündungs- und Autoimmunerkrankungen, septischem Schock, Virusinfektionen und einer fehlerhaften Immunentwicklung in Verbindung gebracht. NF-κB wird auch mit Prozessen der synaptischen Plastizität und des Gedächtnisses in Verbindung gebracht. - 655
Interleukin 8 (IL-8 oder Chemokin (C-X-C-Motiv) Ligand 8, CXCL8) ist ein Chemokin, das von Makrophagen und anderen Zelltypen wie Epithelzellen, glatten Muskelzellen der Atemwege und Endothelzellen produziert wird. Endothelzellen speichern IL-8 in ihren Speicherbläschen, den Weibel-Palade-Körpern. Beim Menschen wird das Interleukin-8-Protein durch das CXCL8-Gen kodiert. IL-8 wird zunächst als Vorläuferpeptid mit 99 Aminosäuren produziert, das dann gespalten wird, um mehrere aktive IL-8-Isoformen zu bilden. In Kultur ist ein Peptid mit 72 Aminosäuren die Hauptform, die von Makrophagen sezerniert wird.
Es gibt viele Rezeptoren auf der Oberflächenmembran, die IL-8 binden können; die am häufigsten untersuchten Typen sind die G-Protein-gekoppelten Serpentinrezeptoren CXCR1 und CXCR2. Expression und Affinität für IL-8 unterscheiden sich zwischen den beiden Rezeptoren (CXCR1 > CXCR2). Über eine Kette von biochemischen Reaktionen wird IL-8 sezerniert und ist ein wichtiger Vermittler der Immunreaktion im Rahmen der angeborenen Immunantwort. - 656
Die Tumor-Nekrose-Faktor (TNF)-Superfamilie ist eine Protein-Superfamilie von Typ-II-Transmembranproteinen, die eine TNF-Homologiedomäne enthalten und Trimere bilden. Mitglieder dieser Superfamilie können durch extrazelluläre proteolytische Spaltung aus der Zellmembran freigesetzt werden und wirken als Zytokin. Diese Proteine werden vor allem von Immunzellen exprimiert und regulieren verschiedene Zellfunktionen, darunter Immunantwort und Entzündung, aber auch Proliferation, Differenzierung, Apoptose und Embryogenese. Die Superfamilie umfasst 19 Mitglieder, die an 29 Mitglieder der TNF-Rezeptor-Superfamilie binden. Das Vorkommen von Orthologen bei Wirbellosen deutet auf einen alten Ursprung dieser Superfamilie in der Evolution hin. Das PROSITE-Muster dieser Superfamilie befindet sich in einem Beta-Sheet im zentralen Abschnitt des Proteins, das bei allen Mitgliedern konserviert ist. - 657
- 658
- 659Lim JS, Nguyen KC, Han JM, Jang IS, Fabian C, Cho KA (December 2015). "Direct Regulation of TLR5 Expression by Caveolin-1". Molecules and Cells. 38 (12): 1111–7. doi:10.14348/molcells.2015.0213. PMC 4697003. PMID 26615831.
- 660Transfettsäuren in der Nahrung. In: labor&more. Nr. 5, 2007, S. 48 (PDF).
- 661science ORF at/Agenturen red: Schädliche Transfette weiter in Nahrungsmitteln. 23. Januar 2023, abgerufen am 25. Januar 2023.
- 662Five billion people unprotected from trans fat leading to heart disease. Abgerufen am 25. Januar 2023 (englisch): „Trans fat intake is responsible for up to 500 000 premature deaths from coronary heart disease each year around the world.“
- 663Wang, Zhong; Gerstein, Mark; Snyder, Michael (January 2009). "RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics". Nature Reviews Genetics. 10 (1): 57–63. doi:10.1038/nrg2484. PMC 2949280. PMID 19015660.
- 664Jiménez-Chillarón, Josep C.; Díaz, Rubén; Ramón-Krauel, Marta (2014). "Chapter 4 - Omics Tools for the Genome-Wide Analysis of Methylation and Histone Modifications". Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry. 64: 81–110. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-62651-6.00004-0. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- 665GK, Sim; FC, Kafatos; CW, Jones; MD, Koehler; A, Efstratiadis; T., Maniatis (December 1979). "Use of a cDNA library for studies on evolution and developmental expression of the chorion multigene families". Cell. 8 (4): 1303–16. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(79)90241-1. PMID 519770.
- 666Jiménez-Chillarón, Josep C.; Díaz, Rubén; Ramón-Krauel, Marta (2014). "Chapter 4 - Omics Tools for the Genome-Wide Analysis of Methylation and Histone Modifications". Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry. 64: 81–110. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-62651-6.00004-0. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- 667Govindarajan, Rajeshwar; Duraiyan, Jeyapradha; Kaliyappan, Karunakaran; Palanisamy, Murugesan (2012). "Microarray and its applications". Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences. 4 (6): S310-2. doi:10.4103/0975-7406.100283. PMC 3467903. PMID 23066278.
- 668C Frith, Martin; Pheasant, Michael; S Mattick, John (2005). "Genomics: The amazing complexity of the human transcriptome". European Journal of Human Genetics. 13 (8): 894–897. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201459. PMID 15970949. S2CID 2836126.
- 669Peralta, Mihaela (2012). "The Human Transcriptome: An Unfinished Story". Genes. 3 (3): 344–360. doi:10.3390/genes3030344. PMC 3422666. PMID 22916334.
- 670Clancy, Suzanne (2008). "DNA Transcription". Nature Education. 1 (11): 41.
- 671Clancy, Suzanne (2008). "DNA Transcription". Nature Education. 1 (11): 41.
- 672Jiménez-Chillarón, Josep C.; Díaz, Rubén; Ramón-Krauel, Marta (2014). "Chapter 4 - Omics Tools for the Genome-Wide Analysis of Methylation and Histone Modifications". Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry. 64: 81–110. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-62651-6.00004-0. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- 673Cellerino & Sanguanini 2018, p. 12
- 674Jiménez-Chillarón, Josep C.; Díaz, Rubén; Ramón-Krauel, Marta (2014). Chapter 4 - Omics Tools for the Genome-Wide Analysis of Methylation and Histone Modifications. Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry. 64: 81–110. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-62651-6.00004-0. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- 675Paul-Ehrlich-Institut: Wie funktionieren mRNA-Impfstoffe und was sind ihre Vorteile?. Auf: pei.de vom 30. Juli 2020; zuletzt abgerufen am 4. Februar 2021
- 676Rein Verbeke, Ine Lentacker, Stefaan C. De Smedt, Heleen Dewitte: Three decades of messenger RNA vaccine development. In: Nano Today. Nr. 28, 2019, S. 100766, doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2019.100766.
- 677Paul-Ehrlich-Institut: Mit welchen Technologien werden humane Virus-Impfstoffe entwickelt? Abschnitt: RNA/DNA-Impfstoffe. Auf: pei.de vom 30. Juli 2020; zuletzt abgerufen am 4. Februar 2021
- 678Kampf gegen Infektionskrankheiten: Erster mRNA-Impfstoff: Diese Technologie könnte Covid-19 besiegen – und nicht nur das. Abgerufen am 2. Dezember 2020.
- 679Fernando P. Polack et al.: Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. In: The New England Journal of Medicine. Dezember 2020, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2034577.
- 680Ugur Sahin et al.: Personalized RNA mutanome vaccines mobilize poly-specific therapeutic immunity against cancer. In: Nature. Band 547, Nr. 7662, Juli 2017, S. 222–226, doi:10.1038/nature23003.
- 681Martin Alberer et al.: Safety and immunogenicity of a mRNA rabies vaccine in healthy adults: an open-label, non-randomised, prospective, first-in-human phase 1 clinical trial. In: The Lancet. Band 390, Nr. 10101, Juli 2017, S. 1511–1520, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31665-3.
- 682Norbert Pardi et al.: Recent advances in mRNA vaccine technology. In: Current Opinion in Immunology. Band 65, August 2020, S. 14–20, doi:10.1016/j.coi.2020.01.008.
- 683Norbert Pardi et al.: mRNA vaccines – a new era in vaccinology. In: Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. Band 17, April 2018, S. 261–279, doi:10.1038/nrd.2017.243.
- 684Oliver Klein und Katja Belousova: Impfstoffe: Warum es keine Langzeit-Nebenwirkungen gibt. In: ZDF. 6. Januar 2021, abgerufen am 14. Januar 2021.
- 685C Frith, Martin; Pheasant, Michael; S Mattick, John (2005). "Genomics: The amazing complexity of the human transcriptome". European Journal of Human Genetics. 13 (8): 894–897. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201459. PMID 15970949. S2CID 2836126.
- 686Berg JMTJ, Stryer L. Biochemistry . New York: W H Freeman, 2002
- 687Mattick JS, Makunin IV. Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet 2006;15 Spec No 1:R17–29
- 688U. Adams, Jill (2008). "Transcriptome: Connecting the Genome to Gene Function". Nature Education. 1 (1): 195.
- 689U. Adams, Jill (2008). "Transcriptome: Connecting the Genome to Gene Function". Nature Education. 1 (1): 195.
- 690Peralta, Mihaela (2012). "The Human Transcriptome: An Unfinished Story". Genes. 3 (3): 344–360. doi:10.3390/genes3030344. PMC 3422666. PMID 22916334.
- 691Wang, Zhong; Gerstein, Mark; Snyder, Michael (January 2009). "RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics". Nature Reviews Genetics. 10 (1): 57–63. doi:10.1038/nrg2484. PMC 2949280. PMID 19015660.
- 692Cellerino & Sanguanini 2018, p. preface
- 693Bryant S, Manning DL (1998). "Isolation of messenger RNA". RNA Isolation and Characterization Protocols. Methods in Molecular Biology. 86. pp. 61–4. doi:10.1385/0-89603-494-1:61. ISBN 978-0-89603-494-5. PMID 9664454.
- 694Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (April 1987). "Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction". Analytical Biochemistry. 162 (1): 156–9. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(87)90021-2. PMID 2440339.
- 695Tachibana, Chris (31 July 2015). "Transcriptomics today: Microarrays, RNA-seq, and more". Science Magazine. 349 (6247): 544. Bibcode:2015Sci...349..544T. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- 696Schena, M.; Shalon, D.; Davis, R. W.; Brown, P. O. (20 October 1995). "Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray". Science. New York, N.Y.). 270 (5235): 467–470. Bibcode:1995Sci...270..467S. doi:10.1126/science.270.5235.467. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 7569999. S2CID 6720459.
- 697Govindarajan, Rajeshwar; Duraiyan, Jeyapradha; Kaliyappan, Karunakaran; Palanisamy, Murugesan (2012). "Microarray and its applications". Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences. 4 (6): S310-2. doi:10.4103/0975-7406.100283. PMC 3467903. PMID 23066278.
- 698Jiménez-Chillarón, Josep C.; Díaz, Rubén; Ramón-Krauel, Marta (2014). "Chapter 4 - Omics Tools for the Genome-Wide Analysis of Methylation and Histone Modifications". Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry. 64: 81–110. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-62651-6.00004-0. Retrieved 25 April 2020.
- 699Cellerino & Sanguanini 2018, p. 12
- 700Cellerino & Sanguanini 2018, p. 12
- 701Cellerino & Sanguanini 2018, p. 12
- 702Cellerino & Sanguanini 2018, p. 13
- 703Cellerino & Sanguanini 2018, p. 13
- 704Cellerino & Sanguanini 2018, p. 12
- 705Cellerino & Sanguanini 2018, p. 18
- 706Kanter, Itamar; Kalisky, Tomer (10 March 2015). "Single Cell Transcriptomics: Methods and Applications". Frontiers in Oncology. 5: 53. doi:10.3389/fonc.2015.00053. ISSN 2234-943X. PMC 4354386. PMID 25806353.
- 707Stegle, Oliver; A. Teichmann, Sarah; C. Marioni, John (2015). "Computational and analytical challenges in single-cell transcriptomics". Nature Reviews Genetics. 16 (3): 133–45. doi:10.1038/nrg3833. PMID 25628217. S2CID 205486032.
- 708Trapnell, Cole (1 October 2015). "Defining cell types and states with single-cell genomics". Genome Research. 25 (10): 1491–1498. doi:10.1101/gr.190595.115. ISSN 1088-9051. PMC 4579334. PMID 26430159.
- 709Kanter, Itamar; Kalisky, Tomer (2015). "Single Cell Transcriptomics: Methods and Applications". Frontiers in Oncology. 5 (13). doi:10.3389/fonc.2015.00053. PMC 4354386. PMID 25806353.
- 710Kanter, Itamar; Kalisky, Tomer (2015). "Single Cell Transcriptomics: Methods and Applications". Frontiers in Oncology. 5 (13). doi:10.3389/fonc.2015.00053. PMC 4354386. PMID 25806353.
- 711Wang, Zhong; Gerstein, Mark; Snyder, Michael (January 2009). "RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics". Nature Reviews Genetics. 10 (1): 57–63. doi:10.1038/nrg2484. PMC 2949280. PMID 19015660.
- 712Wang, Zhong; Gerstein, Mark; Snyder, Michael (January 2009). "RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics". Nature Reviews Genetics. 10 (1): 57–63. doi:10.1038/nrg2484. PMC 2949280. PMID 19015660.
- 713Godoy, Patricio; Schmidt-Heck, Wolfgang; Hellwig, Birte; Nell, Patrick; Feuerborn, David; Rahnenführer, Jörg; Kattler, Kathrin; Walter, Jörn; Blüthgen, Nils; G. Hengstler, Jan (5 July 2018). "Assessment of stem cell differentiation based on genome-wide expression profiles". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 373 (1750): 20170221. doi:10.1098/rstb.2017.0221. PMC 5974444. PMID 29786556.
- 714Zhao, L; Zheng, X; Liu, J; Zheng, R; Yang, R; Wang, Y; Sun, L (1 July 2019). "The placental transcriptome of the first-trimester placenta is affected by in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer". Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology. 17 (1): 50. doi:10.1186/s12958-019-0494-7. PMC 6604150. PMID 31262321.
- 715Eroglu, Binnur; A. Szurek, Edyta; Schall, Peter; E. Latham, Keith; Eroglu, Ali (6 April 2020). "Probing lasting cryoinjuries to oocyte-embryo transcriptome". PLOS ONE. 15 (4): e0231108. Bibcode:2020PLoSO..1531108E. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0231108. PMC 7135251. PMID 32251418.
- 716Szabo, David (2014). "Transcriptomic biomarkers in safety and risk assessment of chemicals". Transcriptomic biomarkers in safety and risk assessment of chemicals. In Ramesh Gupta, editors:Gupta - Biomarkers in Toxicology, Oxford:Academic Press. pp. 1033–1038. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-404630-6.00062-2. ISBN 978-0-12-404630-6.
- 717Drost, Hajk-Georg; Gabel, Alexander; Grosse, Ivo; Quint, Marcel; Grosse, Ivo (2018-05-01). "myTAI: evolutionary transcriptomics with R". Bioinformatics. 34 (9): 1589–1590. doi:10.1093/molbev/msv012. ISSN 0737-4038. PMC 5925770. PMID 29309527.
- 718S, Katayama; et al. (2005). "Antisense Transcription in the Mammalian Transcriptome". Science. 309 (5740): 1564–6. Bibcode:2005Sci...309.1564R. doi:10.1126/science.1112009. PMID 16141073. S2CID 34559885.
- 719Tachibana, Chris (31 July 2015). "Transcriptomics today: Microarrays, RNA-seq, and more". Science Magazine. 349 (6247): 544. Bibcode:2015Sci...349..544T. Retrieved 2 May 2020.
- 720One Thousand Plant Transcriptomes Initiative (23 October 2019). "One thousand plant transcriptomes and the phylogenomics of green plants". Nature. 574 (7780): 679–685. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1693-2. PMC 6872490. PMID 31645766.
- 721Rutley, Nicholas; Twell, David (12 March 2015). "A decade of pollen transcriptomics". Plant Reproduction. 28 (2): 73–89. doi:10.1007/s00497-015-0261-7. PMC 4432081. PMID 25761645.
- 722Cellerino & Sanguanini 2018, p. preface
- 723Crismani, Wayne; Baumann, Ute; Sutton, Tim; Shirley, Neil; Webster, Tracie; Spangenberg, German; Langridge, Peter; A Able, Jason (2006). "Microarray expression analysis of meiosis and microsporogenesis in hexaploid bread wheat". BMC Genomics. 7 (267): 267. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-7-267. PMC 1647286. PMID 17052357.
- 724
- 725Deveshwar, Priyanka; D Bovill, William; Sharma, Rita; A Able, Jason; Kapoor, Sanjay (9 May 2011). "Analysis of anther transcriptomes to identify genes contributing to meiosis and male gametophyte development in rice". BMC Plant Biology. 11 (78): 78. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-11-78. PMC 3112077. PMID 21554676.
- 726
- 727Manzoni, Claudia; A Kia, Demis; Vandrovcova, Jana; Hardy, John; W Wood, Nicholas; A Lewis, Patrick; Ferrari, Raffaele (March 2018). "Genome, transcriptome and proteome: the rise of omics data and their integration in biomedical sciences". Briefings in Bioinformatics. 19 (2): 286–302. doi:10.1093/bib/bbw114. PMC 6018996. PMID 27881428.
- 728Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, Mesirov JP. (2005). Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(43):15545-50.
- 729Schwanhäusser, Björn; et al. (May 2011). "Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control" (PDF). Nature. 473 (7347): 337–342. Bibcode:2011Natur.473..337S. doi:10.1038/nature10098. PMID 21593866. S2CID 205224972.
- 730Einzelnachweis<br>Doris McGartland Rubio, Ellie E. Schoenbaum, Linda S. Lee, David E. Schteingart, Paul R. Marantz: Defining Translational Research: Implications for Training. In: Academic Medicine. Band 85, Nr. 3, März 2010, ISSN 1040-2446, S. 470–475, doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e3181ccd618
- 731Einzelnachweis<br>Jon Leefmann: Was ist Translationale Medizin? Zu Begriff, Geschichte und Epistemologie eines Forschungsparadigmas. In: Markus Wübbeler, Kristina Lippmann, Désirée Wünsch, Dominic Docter (Hrsg.): Lost in Translation? Translationsforschung in den Lebenswissenschaften. 1. Auflage. Schriftenreihe der Jungen Akademie der Wissenschaften und der Literatur – Mainz, Nr. 3. Frank Steiner Verlag, Stuttgart 2019, ISBN 978-3-515-12284-9, S. 119–140
- 732Einzelnachweis<br>Randall J. Cohrs, Tyler Martin, Parviz Ghahramani, Luc Bidaut, Paul J. Higgins und Aamir Shahzad: Translational Medicine definition by the European Society for Translational Medicine, New Horizons in Translational Medicine, März 2015, Band 2 (3), S. 86–88: „An interdisciplinary branch of the biomedical field supported by three main pillars: benchside, bedside and community. The goal of TM is to combine disciplines, resources, expertise, and techniques within these pillars to promote enhancements in prevention, diagnosis, and therapies.“
- 733Hehlgans, T. und Pfeffer, K. (2005): The intriguing biology of the tumour necrosis factor/tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily: players, rules and the games. Immunology 115:1-20. PMID 15819693